| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10807-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10807-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
The pragma EXCEPTION_INIT associates an exception name with an Oracle error number. You can intercept any ORA- error and write a specific handler for it instead of using the OTHERS handler. For more information, see "Associating a PL/SQL Exception with a Number: Pragma EXCEPTION_INIT".
Syntax
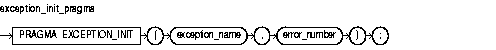
Keyword and Parameter Description
Any valid Oracle error number. These are the same error numbers (always negative) returned by the function SQLCODE.
A user-defined exception declared within the current scope.
Signifies that the statement is a compiler directive.
Usage Notes
You can use EXCEPTION_INIT in the declarative part of any PL/SQL block, subprogram, or package. The pragma must appear in the same declarative part as its associated exception, somewhere after the exception declaration.
Be sure to assign only one exception name to an error number.
Example
The following pragma associates the exception deadlock_detected with Oracle error 60:
DECLARE
deadlock_detected EXCEPTION;
PRAGMA EXCEPTION_INIT(deadlock_detected, -60);
BEGIN
...
EXCEPTION
WHEN deadlock_detected THEN
-- handle the error
...
END;
Related Topics