| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the ALTER PROCEDURE statement to explicitly recompile a standalone stored procedure. Explicit recompilation eliminates the need for implicit run-time recompilation and prevents associated run-time compilation errors and performance overhead.
To recompile a procedure that is part of a package, recompile the entire package using the ALTER PACKAGE statement (see ALTER PACKAGE ).
|
Note: This statement does not change the declaration or definition of an existing procedure. To redeclare or redefine a procedure, use theCREATE PROCEDURE statement with the OR REPLACE clause (see CREATE PROCEDURE ). |
The ALTER PROCEDURE statement is quite similar to the ALTER FUNCTION statement. Please refer to ALTER FUNCTION for more information.
Prerequisites
The procedure must be in your own schema or you must have ALTER ANY PROCEDURE system privilege.
Syntax
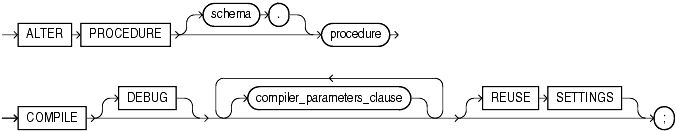
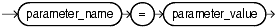
Semantics
Specify the schema containing the procedure. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the procedure is in your own schema.
Specify the name of the procedure to be recompiled.
Specify COMPILE to recompile the procedure. The COMPILE keyword is required. Oracle Database recompiles the procedure regardless of whether it is valid or invalid.
Oracle Database first recompiles objects upon which the procedure depends, if any of those objects are invalid.
Oracle Database also invalidates any local objects that depend upon the procedure, such as procedures that call the recompiled procedure or package bodies that define procedures that call the recompiled procedure.
If Oracle Database recompiles the procedure successfully, then the procedure becomes valid. If recompiling the procedure results in compilation errors, then Oracle Database returns an error and the procedure remains invalid. You can see the associated compiler error messages with the SQL*Plus command SHOW ERRORS.
During recompilation, Oracle Database drops all persistent compiler switch settings, retrieves them again from the session, and stores them at the end of compilation. To avoid this process, specify the REUSE SETTINGS clause.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Concepts for information on how Oracle Database maintains dependencies among schema objects, including remote objects and "Recompiling a Procedure: Example" |
Specify DEBUG to instruct the PL/SQL compiler to generate and store the code for use by the PL/SQL debugger. Specifying this clause is the same as specifying PLSQL_DEBUG = TRUE in the compiler_parameters_clause.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for information on debugging procedures |
Use this clause to specify a value for one of the PL/SQL compiler parameters. The parameters you can specify in this clause are PLSQL_OPTIMIZE_LEVEL, PLSQL_CODE_TYPE, PLSQL_DEBUG, PLSQL_WARNINGS, and NLS_LENGTH_SEMANTICS.
You can specify each parameter only once in each statement. Each setting is valid only for the current library unit being compiled and does not affect other compilations in this session or system. To affect the entire session or system, you must set a value for the parameter using the ALTER SESSION or ALTER SYSTEM statement.
If you omit any parameter from this clause and you specify REUSE SETTINGS, then if a value was specified for the parameter in an earlier compilation of this library unit, Oracle Database uses that earlier value. If you omit any parameter and either you do not specify REUSE SETTINGS or no value has been specified for the parameter in an earlier compilation, then the database obtains the value for that parameter from the session environment.
You cannot set a value for the PLSQL_DEBUG parameter if you also specify DEBUG, because both clauses set the PLSQL_DEBUG parameter, and you can specify a value for each parameter only once.
Specify REUSE SETTINGS to prevent Oracle from dropping and reacquiring compiler switch settings. With this clause, Oracle preserves the existing settings and uses them for the recompilation of any parameters for which values are not specified elsewhere in this statement.
For backward compatibility, Oracle Database sets the persistently stored value of the PLSQL_COMPILER_FLAGS initialization parameter to reflect the values of the PLSQL_CODE_TYPE and PLSQL_DEBUG parameters that result from this statement.
Example
To explicitly recompile the procedure remove_emp owned by the user hr, issue the following statement:
ALTER PROCEDURE hr.remove_emp COMPILE;
If Oracle Database encounters no compilation errors while recompiling credit, then credit becomes valid. Oracle Database can subsequently execute it without recompiling it at run time. If recompiling credit results in compilation errors, then Oracle Database returns an error and credit remains invalid.
Oracle Database also invalidates all dependent objects. These objects include any procedures, functions, and package bodies that call credit. If you subsequently reference one of these objects without first explicitly recompiling it, then Oracle Database recompiles it implicitly at run time.