| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the NOAUDIT statement to stop auditing operations previously enabled by the AUDIT statement.
The NOAUDIT statement must have the same syntax as the previous AUDIT statement. Further, it reverses the effects only of that particular statement. For example, suppose one AUDIT statement A enables auditing for a specific user. A second statement B enables auditing for all users. A NOAUDIT statement C to disable auditing for all users reverses statement B. However, statement C leaves statement A in effect and continues to audit the user that statement A specified.
Prerequisites
To stop auditing of SQL statements, you must have the AUDIT SYSTEM system privilege.
To stop auditing of schema objects, you must be the owner of the object on which you stop auditing or you must have the AUDIT ANY system privilege. In addition, if the object you chose for auditing is a directory, then even if you created it, you must have the AUDIT ANY system privilege.
Syntax
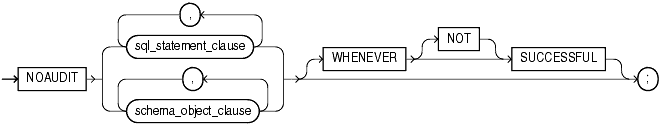
(sql_statement_clause ::=, schema_object_clause ::=)
Semantics
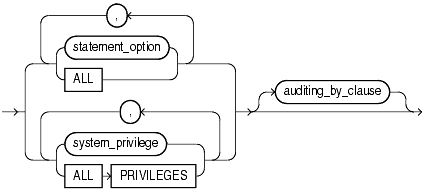
Use the sql_statement_clause to stop auditing of a particular SQL statement.
For statement_option, specify the statement option for which auditing is to be stopped. Please refer to Table 13-1 and Table 13-2 for a list of the statement options and the SQL statements they audit.
Specify ALL to stop auditing of all statement options currently being audited.
For system_privilege, specify the system privilege for which auditing is to be stopped. Please refer to Table 18-1 for a list of the system privileges and the statements they authorize.
Specify ALL PRIVILEGES to stop auditing of all system privileges currently being audited.
Use the auditing_by_clause to stop auditing only those SQL statements issued by particular users. If you omit this clause, then Oracle Database stops auditing all users' statements.
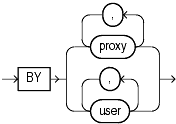
Specify BY user to stop auditing only for SQL statements issued by the specified users in their subsequent sessions. If you omit this clause, then Oracle Database stops auditing for all users' statements, except for the situation described for WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL.
Specify BY proxy to stop auditing only for the SQL statements issued by the specified proxy, on behalf of a specific user or any user.
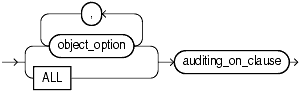
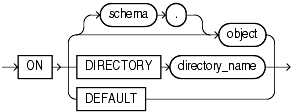
Use the schema_object_clause to stop auditing of a particular database object.
For object_option, specify the type of operation for which auditing is to be stopped on the object specified in the ON clause. Please refer to Table 13-3 for a list of these options.
Specify ALL as a shortcut equivalent to specifying all object options applicable for the type of object.
The auditing_on_clause lets you specify the particular schema object for which auditing is to be stopped.
For object, specify the object name of a table, view, sequence, stored procedure, function, or package, materialized view, or library. If you do not qualify object with schema, then Oracle Database assumes the object is in your own schema. Please refer to AUDIT for information on auditing specific schema objects.
The DIRECTORY clause lets you specify the name of the directory on which auditing is to be stopped.
Specify DEFAULT to remove the specified object options as default object options for subsequently created objects.
Specify WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL to stop auditing only for SQL statements and operations on schema objects that complete successfully.
Specify WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL to stop auditing only for statements and operations that result in Oracle Database errors.
If you omit this clause, then the database stops auditing for all statements or operations, regardless of success or failure.
Examples
If you have chosen auditing for every SQL statement that creates or drops a role, then you can stop auditing of such statements by issuing the following statement:
NOAUDIT ROLE;
If you have chosen auditing for any statement that queries or updates any table issued by the users hr and oe, then you can stop auditing for queries by hr by issuing the following statement:
NOAUDIT SELECT TABLE BY hr;
The preceding statement stops auditing only queries by hr, so the database continues to audit queries and updates by oe as well as updates by hr.
To stop auditing on all statements that are authorized by DELETE ANY TABLE system privilege, issue the following statement:
NOAUDIT DELETE ANY TABLE;
If you have chosen auditing for every SQL statement that queries the employees table in the schema hr, then you can stop auditing for such queries by issuing the following statement:
NOAUDIT SELECT ON hr.employees;
You can stop auditing for queries that complete successfully by issuing the following statement:
NOAUDIT SELECT ON hr.employees WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
This statement stops auditing only for successful queries. Oracle Database continues to audit queries resulting in Oracle Database errors.