| Oracle® Database Recovery Manager Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10770-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Recovery Manager Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10770-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
allocate::=
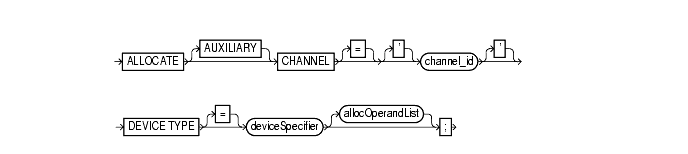
To manually allocate a channel, which is a connection between RMAN and a database instance. Each connection initiates an database server session on the target or auxiliary instance: this server session performs the work of backing up, restoring, or recovering RMAN backups.
Manually allocated channels (allocated by using ALLOCATE) should be distinguished from automatically allocated channels (specified by using CONFIGURE). Manually allocated channels apply only to the RUN job in which you issue the command. Automatic channels apply to any RMAN job in which you do not manually allocate channels. You can always override automatic channel configurations by manually allocating channels within a RUN command.
Each channel operates on one backup set or image copy at a time. RMAN automatically releases the channel at the end of the job.
You can control the degree of parallelism within a job by allocating the desired number of channels. Allocating multiple channels simultaneously allows a single job to read or write multiple backup sets or disk copies in parallel. If you establish multiple connections, then each connection operates on a separate backup set or disk copy.
Whether ALLOCATE CHANNEL causes operating system resources to be allocated immediately depends on the operating system. On some platforms, operating system resources are allocated at the time the command is issued. On other platforms, operating system resources are not allocated until you open a file for reading or writing.
|
Note: When you specify |
ALLOCATE CHANNEL only within the braces of a RUN command.BACKUP, DUPLICATE, CREATE CATALOG, RESTORE, RECOVER, or VALIDATE command.BACKUP DEVICE TYPE or RESTORE DEVICE TYPE to use automatic channels after specifying manual channels with ALLOCATE CHANNEL.ORA_ to a channel name. RMAN reserves channel names beginning with the ORA_ prefix for its own use.| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies a connection between RMAN and an auxiliary database instance. An auxiliary instance is used when executing the See Also: "DUPLICATE" to learn how to duplicate a database, and "CONNECT" to learn how to connect to a duplicate database |
|
|
Specifies a connection between RMAN and the target database instance. Each connection initiates a server session on the database instance: this server session performs the work of backing up, restoring, and recovering backups and copies. Specify a channel id, which is the case-sensitive name of the channel, after the |
|
|
Specifies the type of storage device. See Also: "deviceSpecifier" Note: If you do not specify the |
|
Specifies control options for the allocated channel. See Also: "allocOperandList" |
This command allocates a tape channel for a whole database and archived redo log backup:
RUN { ALLOCATE CHANNEL c1 DEVICE TYPE sbt; BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
}
When backing up to disk, you can spread the backup across several disk drives. Allocate one DEVICE TYPE DISK channel for each disk drive and specify the format string so that the filenames are on different disks:
RUN { ALLOCATE CHANNEL disk1 DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '/disk1/backups/%U'; ALLOCATE CHANNEL disk2 DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '/disk2/backups/%U'; BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG; # AS COPY is default when backing up to disk }
When creating multiple copies of a backup, you can specify the SET BACKUP COPIES command. The following example generates a single backup of the database to disk, and then creates two identical backups of datafile 1 to two different file systems:
RUN { ALLOCATE CHANNEL c1 DEVICE TYPE DISK MAXPIECESIZE 5M; BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG; # AS COPY is the default, so RMAN creates image copies SET BACKUP COPIES = 2; BACKUP DATAFILE 1 FORMAT '/disk1/backups/%U', '/disk2/backups/%U'; }
When creating a duplicate database, allocate a channel by using the AUXILIARY option:
RUN { ALLOCATE AUXILIARY CHANNEL c1 DEVICE TYPE sbt; ALLOCATE AUXILIARY CHANNEL c2 DEVICE TYPE sbt; DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE TO ndbnewh LOGFILE '?/oradata/aux1/redo01.log' SIZE 200K, '?/oradata/aux1/redo02.log' SIZE 200K '?/oradata/aux1/redo03.log' SIZE 200K SKIP READONLY NOFILENAMECHECK; }