| Oracle7 Server Manager User's Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle7 Server Manager User's Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
In the Instance drawer, you can start up and shut down a database, view the values of initialization parameters, resolve in-doubt transactions, and manage users' sessions. This chapter describes the commands available in the Instance drawer's folders:
The SGA is a shared memory region that contains data and control information for an Oracle instance. For more information about the System Global Area, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts.
The following figure illustrates the Database object list.
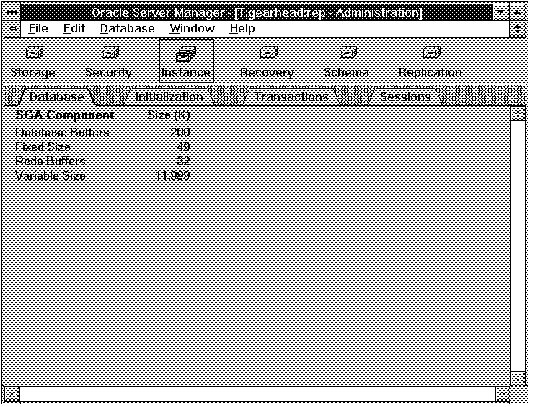 Figure 5 - 1. Database Object List
Figure 5 - 1. Database Object List
SGA Component
The four components of the SGA.
Size (K)
Size of each SGA component in kilobytes.
Attention: If the database is not running, the Database object list contains the message "ORACLE not available."
To start up an instance and optionally mount and open a database, choose Startup from the Database menu. The Startup Database dialog box appears.
The following figure illustrates the Startup Database dialog box.
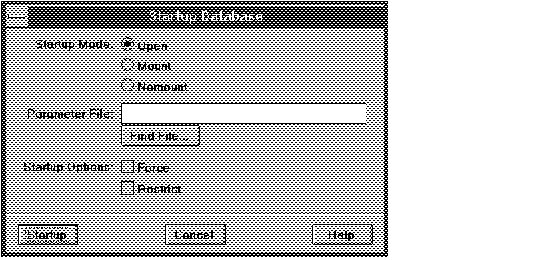 Figure 5 - 2. Startup Database Dialog Box
Figure 5 - 2. Startup Database Dialog Box
Startup Mode: Open
Starts up the instance, and mounts and opens the database.
Startup Mode: Mount
Starts up the instance and mounts the database. The database is accessible only to database administrators.
Startup Mode: Nomount
Starts up the instance, but does not mount the database. Use this mode when you are planning to create a database.
Parameter File
Name of the parameter file used to start the instance. The parameter file must reside on the machine on which you are running Server Manager.
If you do not specify a parameter file, Server Manager looks for the parameter file in the default location for your platform. For information about the default location for the parameter file, see your operating system-specific Oracle documentation.
Find File
Displays the standard file selection dialog box for your platform and allows you to locate the parameter file. For information about the standard file selection dialog box for your system, see your operating system-specific documentation.
Startup Options: Force
Performs a shutdown in abort mode before trying to start the database.
Startup Options: Restrict
Indicates that the database should be opened in restricted mode. In restricted mode, the database is accessible only to users with the RESTRICTED SESSION system privilege.
To shut down a database, choose Shutdown from the Database menu. The Shutdown Database dialog box appears.
The following figure illustrates the Shutdown Database dialog box.
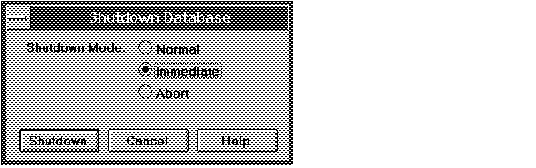 Figure 5 - 3. Shutdown Database Dialog Box
Figure 5 - 3. Shutdown Database Dialog Box
Shutdown Mode: Normal
Shuts down the database in normal mode:
Attention: The Administration Manager, SQL Worksheet, and System Monitors create separate connections when you start them. When performing a shutdown in normal mode, remember to close these windows, or the shutdown will not complete.
Shutdown Mode: Immediate
Shuts down the database in immediate mode:
Shutdown Mode: Abort
Shuts down the database in abort mode:
If you have previously mounted a database, you can open the database by choosing Open from the Database menu. The database is opened and is accessible to all users.
The following figure illustrates the Initialization object list.
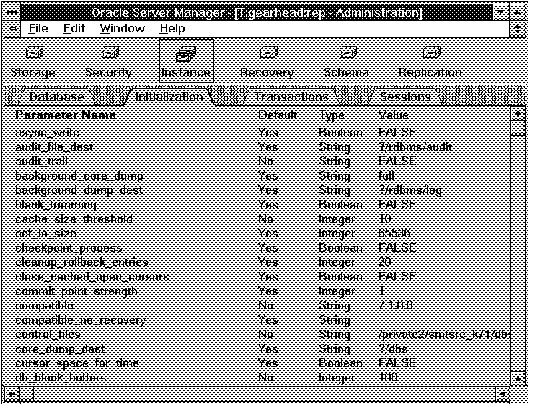 Figure 5 - 4. Initialization Object List
Figure 5 - 4. Initialization Object List
Parameter Name
Name of the initialization parameter.
Default
Whether the parameter's value is the default value.
Type
Datatype of the parameter.
Value
Value of the parameter.
The following figure illustrates the Transaction object list.
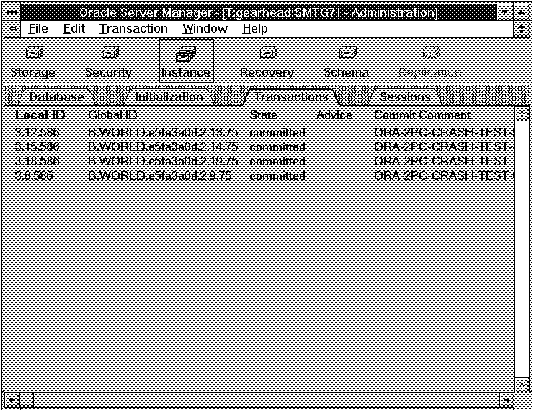 Figure 5 - 5. Transaction Object List
Figure 5 - 5. Transaction Object List
Local ID
Identifier on the local database for the transaction.
Global ID
Global identifier for the transaction.
State
The state of the transaction: collecting, prepared, committed, heuristic commit, or heuristic abort.
Advice
Suggested action: C (Commit), R (Rollback), or null (no advice).
Commit Comment
Comment given with the COMMENT clause of the COMMIT WORK command.
To roll back an in-doubt transaction, select the transaction to be rolled back from the Transaction object list and choose Force Rollback from the Transaction menu.
Attention: You cannot roll back an in-doubt transaction to a savepoint.
The following figure illustrates the Session object list.
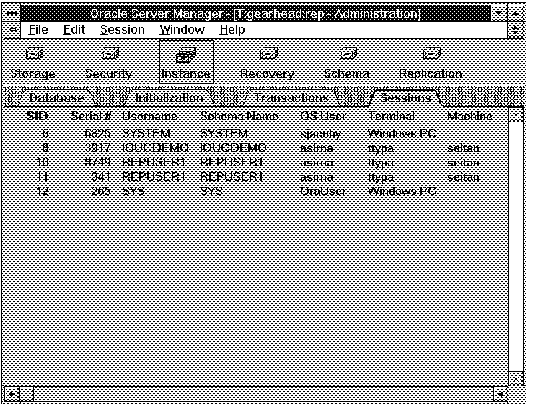 Figure 5 - 6. Session Object List
Figure 5 - 6. Session Object List
SID
Session identifier.
Serial #
Session serial number, used to uniquely identify a session. In combination with the SID, guarantees that session-level commands are applied to the correct session in the event that the session ends and another session begins with the same session identifier.
Username
Oracle username associated with the session.
Schema Name
Schema name associated with the user.
OS User
Operating system username.
Terminal
Operating system terminal name.
Machine
Operating system machine through which the user is connected.
The following figure illustrates the Disconnect Session alert box.
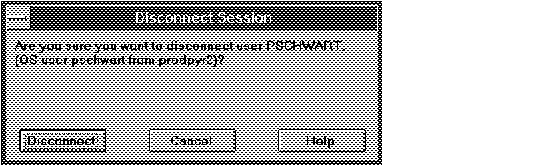 Figure 5 - 7. Disconnect Session Alert Box
Figure 5 - 7. Disconnect Session Alert Box
To make the database accessible to all users, choose Allow All from the Database menu. All users with the CREATE SESSION system privilege are allowed to connect.
|
Prev Next |
Copyright © 1996 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |