| Oracle7 Server Manager User's Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle7 Server Manager User's Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
The information in the Schema drawer is for viewing only. From the Schema drawer, you cannot create, alter, or drop any schema objects. You can create, alter, or drop schema objects using the SQL Worksheet. For a description of the SQL Worksheet, see Chapter 9, "The SQL Worksheet."
This chapter describes the Schema drawer's folders:
Integrity constraints prevent invalid data from being entered into database tables. An integrity constraint is declared on one or more columns in a table, and defines a rule for the data in those columns. For information about data integrity and declarative constraints, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts.
The following figure illustrates the Constraint object list.
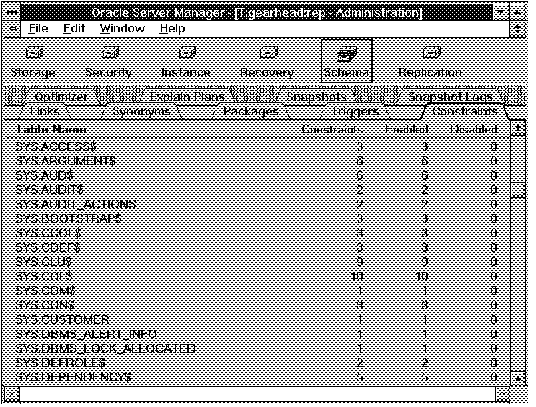 Figure 7 - 1. Constraint Object List
Figure 7 - 1. Constraint Object List
Table Name
Table owner and table name.
Constraints
Number of constraints defined on the table.
Enabled
Number of constraints currently enabled in the table.
Disabled
Number of constraints currently disabled in the table.
A trigger is PL/SQL code that is implicitly executed when inserting, updating, or deleting data in a table. For information about triggers, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts and the Oracle7 Server Application Developer's Guide.
The following figure illustrates the Trigger object list.
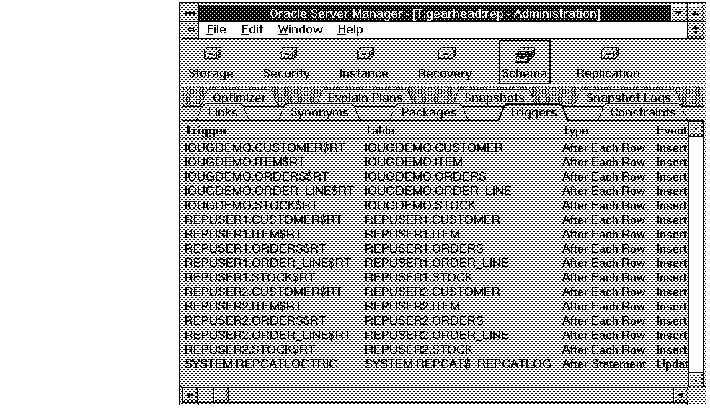 Figure 7 - 2. Trigger Object List
Figure 7 - 2. Trigger Object List
Trigger
Trigger owner and trigger name.
Table
Owner and name of table on which the trigger is defined.
Type
When the trigger fires: Before/After Statement or Before/After Each Row.
Event
Type of statements that fire the trigger: Insert, Update, and/or Delete.
Status
Status of the trigger: Enabled or Disabled.
When
Condition that must be true for the trigger to fire (only applies to row triggers).
A procedure or function is a set of SQL or PL/SQL statements that perform a specific task. A package is a group of related functions, procedures, cursors, and variables. For information about stored procedures, functions, and packages, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts and the Oracle7 Server Application Developer's Guide. For information on PL/SQL, see the PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference.
The following figure illustrates the Packages object list.
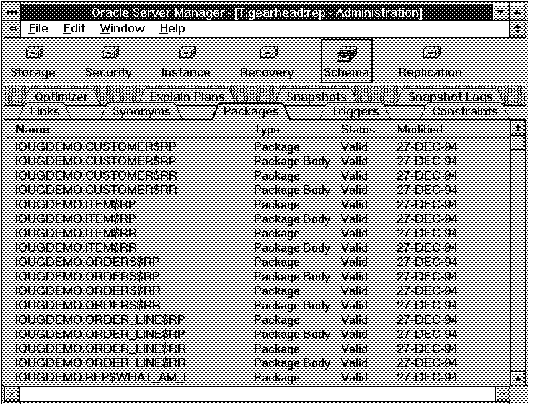 Figure 7 - 3. Package Object List
Figure 7 - 3. Package Object List
Name
Object owner and name of the object.
Type
Type of object: Function, Package, Package Body, or Procedure.
Status
Status of the object: Valid or Invalid (needs to be recompiled).
Modified
Date the object was last modified as the result of a DDL (Data Definition Language) command, including GRANT and REVOKE.
A database link allows you to access a remote database. For information about database links, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts.
The following figure illustrates the Link object list.
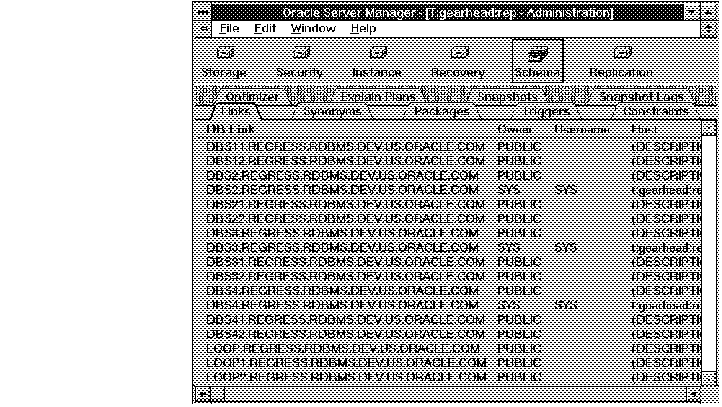 Figure 7 - 4. Link Object List
Figure 7 - 4. Link Object List
DB Link
Name of the database link.
Owner
Owner of the database link.
Username
Name of the user to log in as on the remote database.
Host
SQL*Net service name for the remote database.
Created
Date on which the link was created.
A synonym is an alias for a table, view, snapshot, sequence, procedure function, package, or another synonym. For information about synonyms, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts.
The following figure illustrates the Synonym object list.
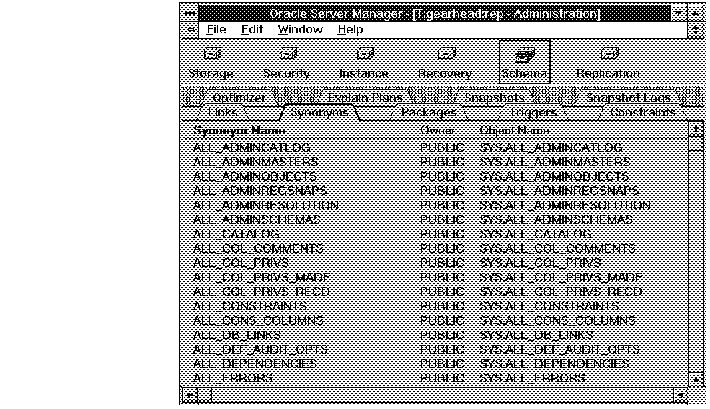 Figure 7 - 5. Synonym Object List
Figure 7 - 5. Synonym Object List
Synonym Name
Name of the synonym.
Owner
Owner of the synonym.
Object Name
Owner and name of the object referenced by the synonym.
DB Link
Name of database link used in a synonym for a remote object.
The Oracle optimizer chooses the execution plan for a SQL statement. When using the cost-based approach, the optimizer can utilize statistics for the objects accessed in the SQL statement. You generate these statistics using the ANALYZE command.
For information about the optimizer and generating statistics, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts and the ANALYZE command in the Oracle7 Server SQL Reference.
The following figure illustrates the Optimizer object list.
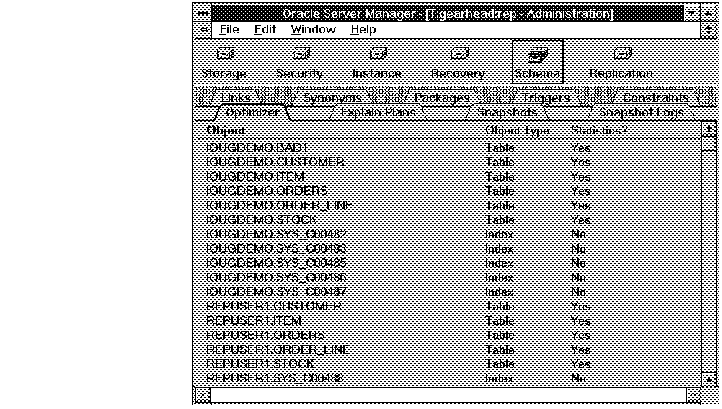 Figure 7 - 6. Optimizer Object List
Figure 7 - 6. Optimizer Object List
Object
The owner and name of the object.
Object Type
Object type: Table, Cluster, or Index.
Statistics?
Whether or not statistics have been generated for the object.
You can use the EXPLAIN PLAN command to generate the execution plan for a particular SQL statement. The execution plan is stored in a table, which by default is called PLAN_TABLE. For information about execution plans and the EXPLAIN PLAN command, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts, the Oracle7 Server Application Developer's Guide, and the Oracle7 Server SQL Reference.
The following figure illustrates the Explain Plan object list.
 Figure 7 - 7. Explain Plan Object List
Figure 7 - 7. Explain Plan Object List
Statement ID
Identifier for the SQL statement (can be null).
Timestamp
Date the EXPLAIN PLAN command was executed for the statement.
Attention: The information displayed in the Explain Plan object list is from the table named PLAN_TABLE belonging to the schema SYS. Server Manager does not display information from any other plan tables. If SYS does not own a PLAN_TABLE or if you do not have access to SYS.PLAN_TABLE, you cannot open the Explain Plans folder.
Additional Information: You can run the script UTLXPLAN.SQL to create a PLAN_TABLE. The location of the script UTLXPLAN.SQL is platform dependent. For information about running UTLXPLAN.SQL, see your operating system-specific Oracle documentation.
A snapshot contains the results of a query of one or more tables or views. The queried tables or views are called the master tables of the snapshot and are often located on remote databases. The snapshot is stored in a table, and can be queried by way of a view defined on the table.
For information about snapshots, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts and the Oracle7 Server Application Developer's Guide.
The following figure illustrates the Snapshot object list.
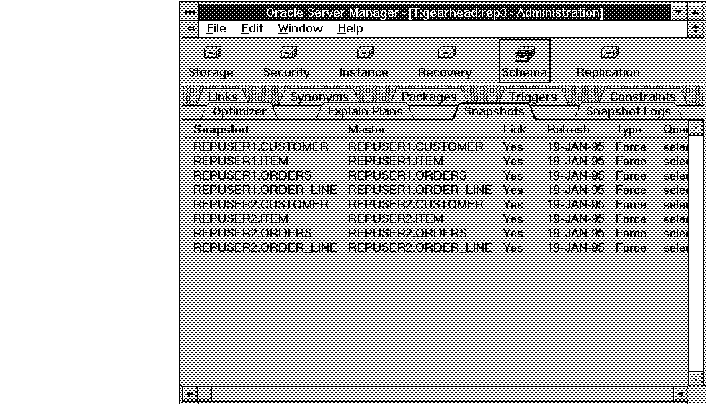 Figure 7 - 8. Snapshot Object List
Figure 7 - 8. Snapshot Object List
Snapshot
Owner of the snapshot and the name of the view associated with the snapshot.
Master
Owner and name of the snapshot's master table.
Link
Whether or not a database link to the master site is used in the snapshot specification.
Refresh
Date of the last refresh (at the master site).
Type
Type of refresh for automatic refreshes: Complete, Fast, or Force.
Query
Original query defining the snapshot.
Attention: You cannot sort the Snapshot object list on the Query column.
A snapshot log is a table associated with the master table of a snapshot. The snapshot log contains information about changes made to its associated master table. The information in the snapshot log is used to refresh the snapshot. For information about snapshot logs, see the Oracle7 Server Concepts and the Oracle7 Server Administrator's Guide.
The following figure illustrates the Snapshot Log object list.
 Figure 7 - 9. Snapshot Log Object List
Figure 7 - 9. Snapshot Log Object List
Table Being Logged
Owner of the snapshot log and master table of the log.
Last Refreshed
Date snapshot was last refreshed (one date for each snapshot defined on the master table).
|
Prev Next |
Copyright © 1996 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |