Release 8.0.5 for Windows NT and Windows 95/98
A64419-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Net8
Getting Started
Release 8.0.5 for Windows NT and Windows 95/98 A64419-01 |
|
This chapter covers the following topics:
Net8 replaces SQL*Net as the networking services and connectivity
component for Oracle8. Net8 has evolved considerably from SQL*Net, supporting
application programming interfaces, Java-enabled Internet browsers and
network services such as naming and security--hence the name change.
Net8 is the foundation of Oracle's family of networking products,
allowing databases and their applications to reside on different computers
and communicate as peer applications. Net8 allows clients to communicate
with Oracle8 and Oracle7 servers through service names, which are
easy to remember aliases for database addresses. Setting up Net8 primarily
involves creating service names for clients so a simple connect string,
such as CONNECT SCOTT/TIGER@SERVICE_NAME, can be used to make a
connection from a client to a server.
Depending on your needs, service names can be stored in a
variety of places, including the Domain Name System (DNS), configuration
files on each client, a centrally located Oracle Names Server, or a non-Oracle
naming service. Wherever you choose to store your service names, Net8 offers
tools to easily configure service names.
The main function of Net8 is to establish sessions and transfer
data between a client and a server or between two servers. Once a session
is established, Net8 acts as a data courier for the client and the server.
The connection operation is initiated during any standard database login
between the client application and the server, with information such as
the client machine name and user name passed to the remote machine.
Sessions are established with the help of a network listener,
located on the server. The network listener brokers the client request,
handing off the request to the server. Every time a client (or server acting
as a client) requests a session with a server, a network listener receives
the actual request. The network listener determines the location of the
server and enables the client to connect to the server. The network listener
is a separate process whose responsibility is to listen for incoming client
connection requests and manage the traffic to the server.
The user requests a database connection from the server by
supplying input (SQL command) through a client-side application such as
SQL*Plus. The application sends the request to Net8 to be
transported across the network to the server. After the connection request
is accepted by the network listener on the server, the client application
requests database information from the server.
The server runs the Oracle8 database software and a Net8
network listener program. The Net8 network listener, through an Oracle
Protocol Adapter, accepts connections from client applications on the network.
Net8 on the server delivers the client data transfer request
to the Oracle8 database. The database performs the function requested by
the user on the client computer. Finally, Net8 transfers the results of
the database functions to the client machine.
Net8, the networking layer formerly known as SQL*Net, uses
the Transparent Network Substrate (TNS) and standard industry network protocols
to connect a client to a server and establish an Oracle session. The following
figure shows the basic connectivity architecture and process, with a connection
request originating from a client side application. The database returns
the queried information in the reverse direction.
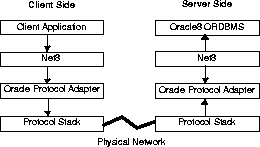
The following is an overview of Oracle network connectivity components:
Net8 is a software layer that is required to communicate
between Oracle clients and servers. The role of Net8 is to establish and
maintain a connection between the client application and the server and
exchange messages between them. It provides both client to server and server
to server communications across any network. It enables client tools to
access, modify, share, and store data on Oracle8 Servers over a network.
The communication between client applications and servers takes place across
one or more networks and is referred to as client/server communication.
The TNS is an underlying layer of Net8 that receives requests
and settles all generic connectivity functions such as opening and closing
a session or sending and receiving requests or responses. TNS then passes
control to an Oracle Protocol Adapter to make the protocol-specific call.
The Oracle Protocol Adapters are responsible for mapping
TNS functionality to industry-standard protocols used in the client/server
connection. Each adapter is responsible for mapping the equivalent functions
between TNS and a specific protocol.
An Oracle Protocol Adapter translates (or adapts):
|
Additional Information: See:
|
The protocol stack (third party software) supplies a reliable
means of communication across the network. All Oracle software in the client/server
connection process requires an existing network protocol stack to make
the machine-level connection between two machines. The network protocol
is responsible only for getting the data from the client machine to the
server machine, at which point the data is passed to the Oracle Protocol
Adapter on the server side.