The view has a setSize method which is like doLayout and setSize in Component combined. The view has a preferenceChanged method which is like invalidate in Component except that one can invalidate just one axis and the child requesting the change is identified.
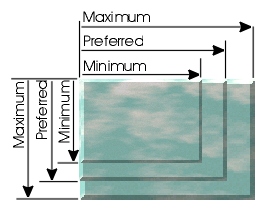
A View expresses the size that it would like to be in terms of three values, a minimum, a preferred, and a maximum span. Layout in a view is can be done independantly upon each axis. For a properly functioning View implementation, the minimum span will be <= the preferred span which in turn will be <= the maximum span.
The minimum set of methods for layout are:
The setSize method should be prepared to be called a number of times (i.e. It may be called even if the size didn't change). The setSize method is generally called to make sure the View layout is complete prior to trying to perform an operation on it that requires an up-to-date layout. A views size should always be set to a value within the minimum and maximum span specified by that view. Additionally, the view must always call the preferenceChanged method on the parent if it has changed the values for the layout it would like, and expects the parent to honor. The parent View is not required to recognize a change until the preferenceChanged has been sent. This allows parent View implementations to cache the child requirements if desired. The calling sequence looks something like the following:
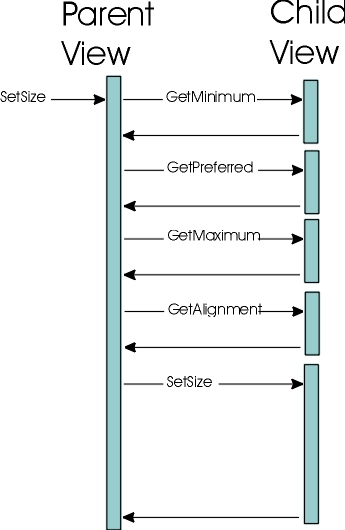
The exact calling sequence is up to the layout functionality of the parent view (if the view has any children). The view may collect the preferences of the children prior to determining what it will give each child, or it might iteratively update the children one at a time.
This is done in the paint method, which is pretty much like a component paint method. Views are expected to potentially populate a fairly large tree. A View has the following semantics for rendering:
- The view gets it's allocation from the parent at paint time, so it must be prepared to redo layout if the allocated area is different from what it is prepared to deal with.
- The coordinate system is the same as the hosting Component (i.e. the Component returned by the getContainer method). This means a child view lives in the same coordinate system as the parent view unless the parent has explicitly changed the coordinate system. To schedule itself to be repainted a view can call repaint on the hosting Component.
- The default is to not clip the children. It is more effecient to allow a view to clip only if it really feels it needs clipping.
- The Graphics object given is not initialized in any way. A view should set any settings needed.
- A View is inherently transparent. While a view may render into it's entire allocation, typically a view does not. Rendering is performed by tranversing down the tree of View implementations. Each View is responsible for rendering it's children. This behavior is depended upon for thread safety. While view implementations do not necessarily have to be implemented with thread safety in mind, other view implementations that do make use of concurrency can depend upon a tree traversal to guarantee thread safety.
- The order of views relative to the model is up to the implementation. Although child views will typically be arranged in the same order that they occur in the model, they may be visually arranged in an entirely different order. View implementations may have Z-Order associated with them if the children are overlapping.
The methods for rendering are:
Because the view objects are produced from a factory and therefore cannot necessarily be counted upon to be in a particular pattern, one must be able to perform translation to properly locate spatial representation of the model. The methods for doing this are:
The layout must be valid prior to attempting to make the translation. The translation is not valid, and must not be attempted while changes are being broadcasted from the model via a DocumentEvent.
If the overall view is represented by many pieces (which is the best situation if one want to be able to change the view and write the least amount of new code), it would be impractical to have a huge number of DocumentListeners. If each view listened to the model, only a few would actually be interested in the changes broadcasted at any given time. Since the model has no knowledge of views, it has no way to filter the broadcast of change information. The view hierarchy itself is instead responsible for propagating the change information. At any level in the view hierarchy, that view knows enough about it's children to best distribute the change information further. Changes are therefore broadcasted starting from the root of the view hierarchy. The methods for doing this are:
| Field Summary | |
static int |
BadBreakWeight
The weight to indicate a view is a bad break opportunity for the purpose of formatting. |
static int |
ExcellentBreakWeight
The weight to indicate a view supports breaking, and this represents a very attractive place to break. |
static int |
ForcedBreakWeight
The weight to indicate a view supports breaking, and must be broken to be represented properly when placed in a view that formats it's children by breaking them. |
static int |
GoodBreakWeight
The weight to indicate a view supports breaking, but better opportunities probably exist. |
static int |
X_AXIS
Axis for format/break operations. |
static int |
Y_AXIS
Axis for format/break operations. |
| Fields inherited from interface javax.swing.SwingConstants |
BOTTOM,
CENTER,
EAST,
HORIZONTAL,
LEADING,
LEFT,
NORTH,
NORTH_EAST,
NORTH_WEST,
RIGHT,
SOUTH,
SOUTH_EAST,
SOUTH_WEST,
TOP,
TRAILING,
VERTICAL,
WEST |
| Constructor Summary | |
View(Element elem)
Creates a new View object. |
|
| Method Summary | |
View |
breakView(int axis,
int offset,
float pos,
float len)
Tries to break this view on the given axis. |
void |
changedUpdate(DocumentEvent e,
Shape a,
ViewFactory f)
Gives notification from the document that attributes were changed in a location that this view is responsible for. |
View |
createFragment(int p0,
int p1)
Create a view that represents a portion of the element. |
float |
getAlignment(int axis)
Determines the desired alignment for this view along an axis. |
AttributeSet |
getAttributes()
Fetches the attributes to use when rendering. |
int |
getBreakWeight(int axis,
float pos,
float len)
Determines how attractive a break opportunity in this view is. |
Shape |
getChildAllocation(int index,
Shape a)
Fetches the allocation for the given child view. |
Container |
getContainer()
Fetches the container hosting the view. |
Document |
getDocument()
Fetches the model associated with the view. |
Element |
getElement()
Fetches the structural portion of the subject that this view is mapped to. |
int |
getEndOffset()
Fetches the portion of the model that this view is responsible for. |
float |
getMaximumSpan(int axis)
Determines the maximum span for this view along an axis. |
float |
getMinimumSpan(int axis)
Determines the minimum span for this view along an axis. |
int |
getNextVisualPositionFrom(int pos,
Position.Bias b,
Shape a,
int direction,
Position.Bias[] biasRet)
Provides a way to determine the next visually represented model location that one might place a caret. |
View |
getParent()
Returns the parent of the view. |
abstract float |
getPreferredSpan(int axis)
Determines the preferred span for this view along an axis. |
int |
getResizeWeight(int axis)
Determines the resizability of the view along the given axis. |
int |
getStartOffset()
Fetches the portion of the model that this view is responsible for. |
View |
getView(int n)
Gets the nth child view. |
int |
getViewCount()
Returns the number of views in this view. |
ViewFactory |
getViewFactory()
Fetches the ViewFactory implementation that is feeding the view hierarchy. |
void |
insertUpdate(DocumentEvent e,
Shape a,
ViewFactory f)
Gives notification that something was inserted into the document in a location that this view is responsible for. |
boolean |
isVisible()
Returns a boolean that indicates whether the view is visible or not. |
Shape |
modelToView(int p0,
Position.Bias b0,
int p1,
Position.Bias b1,
Shape a)
Provides a mapping from the document model coordinate space to the coordinate space of the view mapped to it. |
Shape |
modelToView(int pos,
Shape a)
Deprecated. |
abstract Shape |
modelToView(int pos,
Shape a,
Position.Bias b)
Provides a mapping from the document model coordinate space to the coordinate space of the view mapped to it. |
abstract void |
paint(Graphics g,
Shape allocation)
Renders using the given rendering surface and area on that surface. |
void |
preferenceChanged(View child,
boolean width,
boolean height)
Child views can call this on the parent to indicate that the preference has changed and should be reconsidered for layout. |
void |
removeUpdate(DocumentEvent e,
Shape a,
ViewFactory f)
Gives notification from the document that attributes were removed in a location that this view is responsible for. |
void |
setParent(View parent)
Establishes the parent view for this view. |
void |
setSize(float width,
float height)
Sets the size of the view. |
int |
viewToModel(float x,
float y,
Shape a)
Deprecated. |
abstract int |
viewToModel(float x,
float y,
Shape a,
Position.Bias[] biasReturn)
Provides a mapping from the view coordinate space to the logical coordinate space of the model. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
clone,
equals,
finalize,
getClass,
hashCode,
notify,
notifyAll,
toString,
wait,
wait,
wait |
| Field Detail |
BadBreakWeight
public static final int BadBreakWeight
- The weight to indicate a view is a bad break
opportunity for the purpose of formatting. This
value indicates that no attempt should be made to
break the view into fragments as the view has
not been written to support fragmenting.
- See Also:
getBreakWeight(int, float, float),GoodBreakWeight,ExcellentBreakWeight,ForcedBreakWeight
GoodBreakWeight
public static final int GoodBreakWeight
- The weight to indicate a view supports breaking,
but better opportunities probably exist.
- See Also:
getBreakWeight(int, float, float),BadBreakWeight,GoodBreakWeight,ExcellentBreakWeight,ForcedBreakWeight
ExcellentBreakWeight
public static final int ExcellentBreakWeight
- The weight to indicate a view supports breaking,
and this represents a very attractive place to
break.
- See Also:
getBreakWeight(int, float, float),BadBreakWeight,GoodBreakWeight,ExcellentBreakWeight,ForcedBreakWeight
ForcedBreakWeight
public static final int ForcedBreakWeight
- The weight to indicate a view supports breaking,
and must be broken to be represented properly
when placed in a view that formats it's children
by breaking them.
- See Also:
getBreakWeight(int, float, float),BadBreakWeight,GoodBreakWeight,ExcellentBreakWeight,ForcedBreakWeight
X_AXIS
public static final int X_AXIS
- Axis for format/break operations.
Y_AXIS
public static final int Y_AXIS
- Axis for format/break operations.
| Constructor Detail |
View
public View(Element elem)
- Creates a new View object.
- Parameters:
elem- the element to represent
| Method Detail |
getParent
public View getParent()
- Returns the parent of the view.
- Returns:
- the parent, null if none
isVisible
public boolean isVisible()
- Returns a boolean that indicates whether
the view is visible or not. By default
all views are visible.
- Returns:
- boolean value.
getPreferredSpan
public abstract float getPreferredSpan(int axis)
- Determines the preferred span for this view along an
axis.
- Parameters:
axis- may be either View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXIS- See Also:
getPreferredSpan(int)
getMinimumSpan
public float getMinimumSpan(int axis)
- Determines the minimum span for this view along an
axis.
- Parameters:
axis- may be either View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXIS- See Also:
getPreferredSpan(int)
getMaximumSpan
public float getMaximumSpan(int axis)
- Determines the maximum span for this view along an
axis.
- Parameters:
axis- may be either View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXIS- See Also:
getPreferredSpan(int)
preferenceChanged
public void preferenceChanged(View child,
boolean width,
boolean height)
- Child views can call this on the parent to indicate that
the preference has changed and should be reconsidered
for layout. By default this just propagates upward to
the next parent. The root view will call
revalidateon the associated text component.- Parameters:
child- the child viewwidth- true if the width preference has changedheight- true if the height preference has changed- See Also:
JComponent.revalidate()
getAlignment
public float getAlignment(int axis)
- Determines the desired alignment for this view along an
axis. By default this is simply centered.
- Parameters:
axis- may be either View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXIS
paint
public abstract void paint(Graphics g,
Shape allocation)
- Renders using the given rendering surface and area on that
surface. The view may need to do layout and create child
views to enable itself to render into the given allocation.
- Parameters:
g- the rendering surface to useallocation- the allocated region to render into- See Also:
paint(java.awt.Graphics, java.awt.Shape)
setParent
public void setParent(View parent)
- Establishes the parent view for this view. This is
guaranteed to be called before any other methods if the
parent view is functioning properly. This is also
the last method called, since it is called to indicate
the view has been removed from the hierarchy as
well. If this is reimplemented,
super.setParent()should be called.- Parameters:
parent- the new parent, or null if the view is being removed from a parent it was previously added to
getViewCount
public int getViewCount()
- Returns the number of views in this view. Since
the default is to not be a composite view this
returns 0.
- Returns:
- the number of views >= 0
- See Also:
getViewCount()
getView
public View getView(int n)
- Gets the nth child view. Since there are no
children by default, this returns null.
- Parameters:
n- the number of the view to get, >= 0 && < getViewCount()- Returns:
- the view
getChildAllocation
public Shape getChildAllocation(int index,
Shape a)
- Fetches the allocation for the given child view.
This enables finding out where various views
are located, without assuming the views store
their location. This returns null since the
default is to not have any child views.
- Parameters:
index- the index of the child, >= 0 && < getViewCount()a- the allocation to this view.- Returns:
- the allocation to the child
getNextVisualPositionFrom
public int getNextVisualPositionFrom(int pos,
Position.Bias b,
Shape a,
int direction,
Position.Bias[] biasRet)
throws BadLocationException
- Provides a way to determine the next visually represented model
location that one might place a caret. Some views may not be visible,
they might not be in the same order found in the model, or they just
might not allow access to some of the locations in the model.
- Parameters:
pos- the position to convert >= 0a- the allocated region to render intodirection- the direction from the current position that can be thought of as the arrow keys typically found on a keyboard. This may be SwingConstants.WEST, SwingConstants.EAST, SwingConstants.NORTH, or SwingConstants.SOUTH.- Returns:
- the location within the model that best represents the next location visual position.
- Throws:
- BadLocationException -
- IllegalArgumentException - for an invalid direction
modelToView
public abstract Shape modelToView(int pos,
Shape a,
Position.Bias b)
throws BadLocationException
- Provides a mapping from the document model coordinate space
to the coordinate space of the view mapped to it.
- Parameters:
pos- the position to convert >= 0a- the allocated region to render intob- the bias toward the previous character or the next character represented by the offset, in case the position is a boundary of two views.- Returns:
- the bounding box of the given position is returned
- Throws:
- BadLocationException - if the given position does
not represent a valid location in the associated document
- IllegalArgumentException - for an invalid bias argument
- See Also:
viewToModel(float, float, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.Position.Bias[])
modelToView
public Shape modelToView(int p0,
Position.Bias b0,
int p1,
Position.Bias b1,
Shape a)
throws BadLocationException
- Provides a mapping from the document model coordinate space
to the coordinate space of the view mapped to it.
- Parameters:
p0- the position to convert >= 0b0- the bias toward the previous character or the next character represented by p0, in case the position is a boundary of two views.p1- the position to convert >= 0b1- the bias toward the previous character or the next character represented by p1, in case the position is a boundary of two views.a- the allocated region to render into- Returns:
- the bounding box of the given position is returned
- Throws:
- BadLocationException - if the given position does
not represent a valid location in the associated document
- IllegalArgumentException - for an invalid bias argument
- See Also:
viewToModel(float, float, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.Position.Bias[])
viewToModel
public abstract int viewToModel(float x,
float y,
Shape a,
Position.Bias[] biasReturn)
- Provides a mapping from the view coordinate space to the logical
coordinate space of the model. The biasReturn argument will be
filled in to indicate that the point given is closer to the next
character in the model or the previous character in the model.
- Parameters:
x- the X coordinate >= 0y- the Y coordinate >= 0a- the allocated region to render into- Returns:
- the location within the model that best represents the given point in the view >= 0. The biasReturn argument will be filled in to indicate that the point given is closer to the next character in the model or the previous character in the model.
insertUpdate
public void insertUpdate(DocumentEvent e,
Shape a,
ViewFactory f)
- Gives notification that something was inserted into the document
in a location that this view is responsible for.
- Parameters:
e- the change information from the associated documenta- the current allocation of the viewf- the factory to use to rebuild if the view has children- See Also:
insertUpdate(javax.swing.event.DocumentEvent, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.ViewFactory)
removeUpdate
public void removeUpdate(DocumentEvent e,
Shape a,
ViewFactory f)
- Gives notification from the document that attributes were removed
in a location that this view is responsible for.
- Parameters:
e- the change information from the associated documenta- the current allocation of the viewf- the factory to use to rebuild if the view has children- See Also:
removeUpdate(javax.swing.event.DocumentEvent, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.ViewFactory)
changedUpdate
public void changedUpdate(DocumentEvent e,
Shape a,
ViewFactory f)
- Gives notification from the document that attributes were changed
in a location that this view is responsible for.
- Parameters:
e- the change information from the associated documenta- the current allocation of the viewf- the factory to use to rebuild if the view has children- See Also:
changedUpdate(javax.swing.event.DocumentEvent, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.ViewFactory)
getDocument
public Document getDocument()
- Fetches the model associated with the view.
- Returns:
- the view model, null if none
- See Also:
getDocument()
getStartOffset
public int getStartOffset()
- Fetches the portion of the model that this view is
responsible for.
- Returns:
- the starting offset into the model >= 0
- See Also:
getStartOffset()
getEndOffset
public int getEndOffset()
- Fetches the portion of the model that this view is
responsible for.
- Returns:
- the ending offset into the model >= 0
- See Also:
getEndOffset()
getElement
public Element getElement()
- Fetches the structural portion of the subject that this
view is mapped to. The view may not be responsible for the
entire portion of the element.
- Returns:
- the subject
- See Also:
getElement()
getAttributes
public AttributeSet getAttributes()
- Fetches the attributes to use when rendering. By default
this simply returns the attributes of the associated element.
This method should be used rather than using the element
directly to obtain access to the attributes to allow
view-specific attributes to be mixed in or to allow the
view to have view-specific conversion of attributes by
subclasses.
Each view should document what attributes it recognizes
for the purpose of rendering or layout, and should always
access them through the AttributeSet returned by this method.
breakView
public View breakView(int axis,
int offset,
float pos,
float len)
- Tries to break this view on the given axis. This is
called by views that try to do formatting of their
children. For example, a view of a paragraph will
typically try to place its children into row and
views representing chunks of text can sometimes be
broken down into smaller pieces.
This is implemented to return the view itself, which represents the default behavior on not being breakable. If the view does support breaking, the starting offset of the view returned should be the given offset, and the end offset should be less than or equal to the end offset of the view being broken.
- Parameters:
axis- may be either View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXISoffset- the location in the document model that a broken fragment would occupy >= 0. This would be the starting offset of the fragment returned.pos- the position along the axis that the broken view would occupy >= 0. This may be useful for things like tab calculations.len- specifies the distance along the axis where a potential break is desired >= 0.- Returns:
- the fragment of the view that represents the given span, if the view can be broken. If the view doesn't support breaking behavior, the view itself is returned.
- See Also:
ParagraphView
createFragment
public View createFragment(int p0,
int p1)
- Create a view that represents a portion of the element.
This is potentially useful during formatting operations
for taking measurements of fragments of the view. If
the view doesn't support fragmenting (the default), it
should return itself.
- Parameters:
p0- the starting offset >= 0. This should be a value greater or equal to the element starting offset and less than the element ending offset.p1- the ending offset > p0. This should be a value less than or equal to the elements end offset and greater than the elements starting offset.- See Also:
LabelView
getBreakWeight
public int getBreakWeight(int axis,
float pos,
float len)
- Determines how attractive a break opportunity in
this view is. This can be used for determining which
view is the most attractive to call
breakViewon in the process of formatting. A view that represents text that has whitespace in it might be more attractive than a view that has no whitespace, for example. The higher the weight, the more attractive the break. A value equal to or lower thanBadBreakWeightshould not be considered for a break. A value greater than or equal toForcedBreakWeightshould be broken.This is implemented to provide the default behavior of returning
BadBreakWeightunless the length is greater than the length of the view in which case the entire view represents the fragment. Unless a view has been written to support breaking behavior, it is not attractive to try and break the view. An example of a view that does support breaking isLabelView. An example of a view that uses break weight isParagraphView.- Parameters:
axis- may be either View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXISpos- the potential location of the start of the broken view >= 0. This may be useful for calculating tab positions.len- specifies the relative length from pos where a potential break is desired >= 0.- Returns:
- the weight, which should be a value between ForcedBreakWeight and BadBreakWeight.
- See Also:
LabelView,ParagraphView,BadBreakWeight,GoodBreakWeight,ExcellentBreakWeight,ForcedBreakWeight
getResizeWeight
public int getResizeWeight(int axis)
- Determines the resizability of the view along the
given axis. A value of 0 or less is not resizable.
- Parameters:
axis- View.X_AXIS or View.Y_AXIS- Returns:
- the weight
setSize
public void setSize(float width,
float height)
- Sets the size of the view. This should cause
layout of the view, if it has any layout duties.
The default is to do nothing.
- Parameters:
width- the width >= 0height- the height >= 0
getContainer
public Container getContainer()
- Fetches the container hosting the view. This is useful for
things like scheduling a repaint, finding out the host
components font, etc. The default implementation
of this is to forward the query to the parent view.
- Returns:
- the container, null if none
getViewFactory
public ViewFactory getViewFactory()
- Fetches the ViewFactory implementation that is feeding
the view hierarchy. Normally the views are given this
as an argument to updates from the model when they
are most likely to need the factory, but this
method serves to provide it at other times.
- Returns:
- the factory, null if none
modelToView
public Shape modelToView(int pos,
Shape a)
throws BadLocationException
- Deprecated.
- Provides a mapping from the document model coordinate space to the coordinate space of the view mapped to it. This is implemented to default the bias to Position.Bias.Forward which was previously implied.
- Parameters:
pos- the position to convert >= 0a- the allocated region to render into- Returns:
- the bounding box of the given position is returned
- Throws:
- BadLocationException - if the given position does not represent a valid location in the associated document
- See Also:
modelToView(int, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.Position.Bias)
- Provides a mapping from the document model coordinate space to the coordinate space of the view mapped to it. This is implemented to default the bias to Position.Bias.Forward which was previously implied.
viewToModel
public int viewToModel(float x,
float y,
Shape a)
- Deprecated.
- Provides a mapping from the view coordinate space to the logical coordinate space of the model.
- Parameters:
x- the X coordinate >= 0y- the Y coordinate >= 0a- the allocated region to render into- Returns:
- the location within the model that best represents the given point in the view >= 0
- See Also:
viewToModel(float, float, java.awt.Shape, javax.swing.text.Position.Bias[])
- Provides a mapping from the view coordinate space to the logical coordinate space of the model.
|
JavaTM 2 Platform Standard Edition |
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
Submit a bug or feature
Java, Java 2D, and JDBC are a trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the US and other countries.
Copyright 1993-1999 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 901 San Antonio Road,
Palo Alto, California, 94303, U.S.A. All Rights Reserved.