

 
|
The QGridLayout class lays out widgets in a grid. More...
#include <qlayout.h>
Inherits QLayout.
QGridLayout takes the space it gets (from its parent layout or from the mainWidget()), divides it up into rows and columns, and puts each of the widgets it manages into the correct cell(s).
Columns and rows behave identically; we will discuss columns but there are equivalent functions for rows.
Each column has a minimum width and a stretch factor. The minimum width is the greatest of that set using addColSpacing() and the minimum width of each widget in that column. The stretch factor is set using setColStretch() and determines how much of the available space the column will get, over and above its necessary minimum.
Normally, each managed widget or layout is put into a cell of its own using addWidget(), addLayout(), or by the auto-add facility, but you can also put widget into multiple cells using addMultiCellWidget(). If you do that, QGridLayout will make a guess at how to distribute the size over the columns/rows (based on the stretch factors). You can adjust the minimum width of each column/row using addColSpacing()/addRowSpacing().
This illustration shows a fragment of a dialog with a five-column, three-row grid (the grid is shown overlaid in magenta):
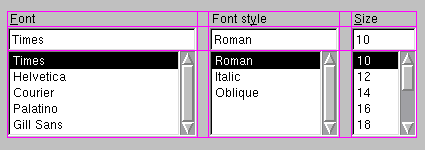
Columns 0, 2 and 4 in this dialog fragment are made up of a QLabel, a QLineEdit and a QListBox. Columns 1 and 2 are placeholders, made with addColSpacing(). Row 0 consists of three QLabel objects, row 1 of three QLineEdit objects and row 2 of three QListBox objects.
Since we did not want any space between the rows, we had to use placeholder columns to get the right amount of space between the columns.
Note that the columns and rows are not equally wide/tall: If you want two columns to be equally wide, you must set the columns' minimum widths and stretch factors to be the same yourself. You do this using addColSpacing() and setStretch().
If the QGridLayout is not the top-level layout (ie. is not managing all of the widget's area and children), you must add it to its parent layout when you have created it, but before you can do anything with it. The normal way to add a layout is by calling parentLayout->addLayout().
Once you have done that, you can start putting widgets and other layouts in the cells of your grid layout using addWidget(), addLayout() and addMultiCellWidget().
QGridLayout also includes two margin widths: The border width and the inter-box width. The border width is the width of the reserved space along each of the QGridLayout's four sides. The intra-widget width is the width of the automatically allocated spacing between neighbouring boxes.
The border width defaults to 0, and the intra-widget width defaults to the same as the border width. Both are set using arguments to the constructor.
See also the Layout Overview documentation.
Examples: cursor/cursor.cpp layout/layout.cpp rot13/rot13.cpp
Constructs a new grid that is placed inside parentLayout, with nRows rows and nCols columns, If space is -1, this QGridLayout will inherits its parent's spacing(), otherwise space is used.
This grid is placed according to parentLayout's default placement rules.
Constructs a new QGridLayout with nRows rows, nCols columns and main widget parent. parent may not be 0.
border is the number of pixels between the edge of the widget and the managed children. space is the default number of pixels between cells. If space is -1 the value of border is used.
name is the internal object name.
Constructs a new grid with nRows rows and nCols columns, If space is -1, this QGridLayout will inherits its parent's spacing(), otherwise space is used.
You have to insert this grid into another layout. You can insert widgets and layouts in this layout at any time, but layout will not be performed before it is inserted.
Destructs the grid layout. Geometry management is terminated if this is a top-level grid.
[protected]Adds item at position row, col. The layout takes over ownership of item.
Sets the minimum width of col to minsize pixels.
[virtual]Adds item to the next free position of this layout.
Reimplemented from QLayout.
Adds item at position row, col. The layout takes over ownership of item.
Places another layout at position (row, col) in the grid. The top left position is (0,0).
Adds the item to the cell grid, spanning multiple rows/columns.
Alignment is specified by alignment which is a bitwise OR of Qt::AlignmentFlags values. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
Adds the layout w to the cell grid, spanning multiple rows/columns.
Alignment is specified by alignment which is a bitwise OR of Qt::AlignmentFlags values. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
A non-zero alignment indicates that the layout should not grow to fill the available space, but should be sized according to sizeHint().
Adds the widget w to the cell grid, spanning multiple rows/columns.
Alignment is specified by alignment which is a bitwise OR of Qt::AlignmentFlags values. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
A non-zero alignment indicates that the widget should not grow to fill the available space, but should be sized according to sizeHint().
Examples: cursor/cursor.cpp layout/layout.cpp
Sets the minimum height of row to minsize pixels.
Adds the widget w to the cell grid at row, col. The top left position is (0,0)
Alignment is specified by alignment which is a bitwise OR of Qt::AlignmentFlags values. The default alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
Note 1: You should not call this if you have enabled the auto-add facility of the layout.
Note 2: The alignment parameter is interpreted more aggressively than in previous versions of Qt. A non-default alignment now indicates that the widget should not grow to fill the available space, but should be sized according to sizeHint().
Examples: cursor/cursor.cpp layout/layout.cpp rot13/rot13.cpp
Returns the geometry of the cell with row row, and column col in the grid. Returns an invalid rectangle if row or col is outside the grid.
Warning: in the current version of Qt, this function does not return valid results until setGeometry() has been called, ie. after the mainWidget() is visible.
Returns the stretch factor for column col.
See also setColStretch().
Expands this grid so that it will have nRows rows and nCols columns. Will not shrink the grid. You should not need to call this function, as QGridLayout expands automatically as new items are inserted.
[virtual]Returns the expansiveness of this layout.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
[protected]Searches for w in this layout (not including child layouts). If w is found, it sets row and col to the row and column and returns TRUE. If w is not found, FALSE is returned.
Warning: If a widget spans multiple rows/columns, the top-left cell is returned.
[virtual]Returns whether this layout's preferred height depends on its width.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
[virtual]Returns the layout's preferred height when it is w pixels wide.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
[virtual]Resets cached information.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
[virtual]Reimplemented for internal reasons; the API is not affected.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
[virtual]Returns the maximum size needed by this grid.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
[virtual]Returns the minimum size needed by this grid.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
Returns the number of columns in this grid.
Returns the number of rows in this grid.
Returns the stretch factor for row row.
See also setRowStretch().
[virtual]Sets the stretch factor of column col to stretch. The first column is number 0.
The stretch factor is relative to the other columns in this grid. Columns with higher stretch factor take more of the available space.
The default stretch factor is 0. If the stretch factor is 0 and no other column in this table can grow at all, the column may still grow.
See also colStretch(), addColSpacing() and setRowStretch().
Examples: layout/layout.cpp
[virtual]Resizes managed widgets within the rectangle r.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
Sets which of the four corners of the grid corresponds to (0,0).
[virtual]Sets the stretch factor of row row to stretch. The first row is number 0.
The stretch factor is relative to the other rows in this grid. Rows with higher stretch factor take more of the available space.
The default stretch factor is 0. If the stretch factor is 0 and no other row in this table can grow at all, the row may still grow.
See also rowStretch(), addRowSpacing() and setColStretch().
[virtual]Returns the preferred size of this grid.
Reimplemented from QLayoutItem.
Search the documentation, FAQ, qt-interest archive and more (uses
www.trolltech.com):
This file is part of the Qt toolkit, copyright © 1995-2000 Trolltech, all rights reserved.
| Copyright © 2000 Trolltech | Trademarks | Qt version 2.2.1
|