Release 2.4
A63820-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8
ConText Cartridge Administrator's Guide
Release 2.4 A63820-01 |
|
This chapter introduces Oracle8 ConText Cartridge and discusses
the various administration tasks that you may need to perform for your
ConText system.
The topics covered in this chapter are:
ConText is an Oracle server option which enables text queries
to be performed through SQL and PL/SQL from most Oracle interfaces.
By installing ConText with an Oracle server, client tools
such as SQL*Plus, Oracle Forms, and Pro*C are able to retrieve and manipulate
text in an Oracle database. Most tools which can call an Oracle stored
procedure can perform text queries and other text operations.
ConText manages textual data in concert with traditional
datatypes in an Oracle database. When text is inserted, updated, or deleted,
ConText automatically manages the change.
ConText provides advanced indexing, analysis, retrieval, and viewing functionality that can be integrated into any text applications that use Oracle8. The list of features include:
| See
Also:
For more information about text retrieval, linguistic analysis, highlighting, and document viewing, see Oracle8 ConText Cartridge Application Developer's Guide. |
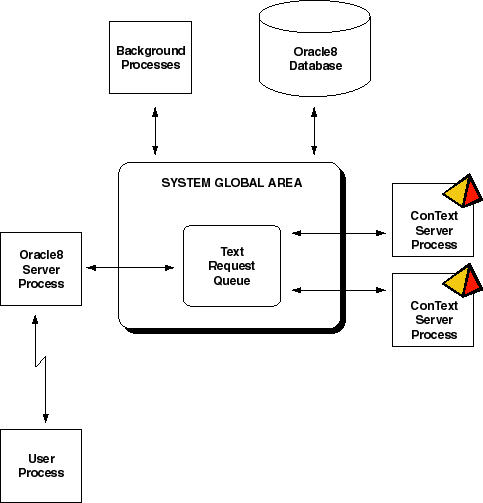
The ConText process model uses the Oracle server model with
the addition of one or more ConText server processes and a queue for handling
text operations.
ConText can be used in both dedicated server (one server
process for each user process) and multi-threaded server environments (dispatcher,
shared server, and background processes).
This diagram shows ConText servers and the Text Request Queue
working in concert with an Oracle server process in a dedicated server
environment.
In the standard Oracle server model, when a user process
connects to the database, it spawns a dedicated server process which handles
all incoming requests from the user process.
With ConText, if a request comes in that includes a text
operation, the request is picked up by the server process for the user
process. The server process sends the request to the Text Request Queue
for processing by the next available ConText server processes.
For example, a text query is submitted by a user. The query
is picked up by the Oracle server process and sent to the Text Request
Queue.
The first available ConText server picks up the text query
from the Text Request Queue and processes it. The results from the text
query are then returned to the user process.
| See
Also:
For more information about ConText servers, see "ConText Servers" in Chapter 2, "Administration Concepts". For more information about text operations, see "Text Operations" in Chapter 6, "Text Concepts". For more information about the Oracle server model, see Oracle8 Concepts. |
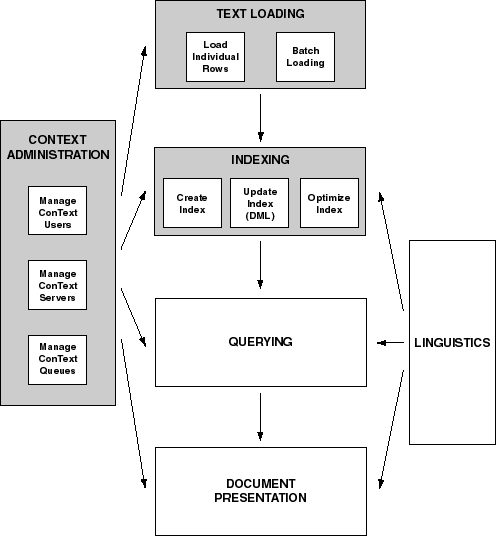
Figure 1-1 illustrates the six main functional areas of ConText:
Oracle8 ConText Cartridge Administrator's Guide provides
details about and instructions for the tasks that can be performed in ConText
administration, text loading, and indexing. These tasks may be performed
by a single user or may be divided between different users/responsibilities.
The remaining three areas, querying, document presentation,
and Linguistics, are typically part of a ConText application and are described
in full in Oracle8 ConText Cartridge Application
Developer's Guide.
ConText administration includes the following tasks, which
are covered in Part 1 of this manual:
| See
Also:
For examples of performing the ConText administration tasks from the command-line, see Chapter 3, "Administering ConText". For more information about ConText users, servers, and queues, see Chapter 2, "Administration Concepts". |
ConText administration tasks are always performed by the
ConText administrator, who may be the system and/or database administrator
or a separate user.
Text loading includes the following tasks, which are covered
in Part II of this manual:
| See
Also:
For examples of performing the text loading tasks from the command-line, see Chapter 9, "Setting Up and Managing Text". For more information about loading text, see Chapter 6, "Text Concepts". For more information about sources and other text loading objects in the ConText data dictionary, see Chapter 7, "Automated Text Loading". |
Text loading may be performed by the ConText administrator
because it requires access to system and database resources or it may be
performed by application developers.
For example, loading text into the database requires access
to the appropriate tables.
In addition, automated text loading requires ConText servers
to be running with the appropriate designation and only ConText administrators
can manage ConText servers.
However, an application may provide users with the ability
to load/update text for an individual file, which requires the application
developer to build the functionality into the application.
Indexing includes the following tasks, which are covered
in Part II of this manual:
| See
Also:
For examples of performing the indexing tasks from the command-line, see Chapter 9, "Setting Up and Managing Text". For more information about text columns and ConText indexes, see Chapter 6, "Text Concepts". For more information about preferences, policies, and other text loading objects in the ConText data dictionary, see Chapter 8, "ConText Indexing". |
Indexing may be performed by the ConText administrator because
they require access to system and database resources.
For example, creating indexes requires ConText servers to
be running with the appropriate designation and only ConText administrators
can manage ConText servers.
However, some tasks, such as defining policies and preferences,
may be performed by application developers because the options used to
create a index have an effect on how an application retrieves text.
ConText provides two different methods for performing the administration tasks associated with ConText administration, text loading, and indexing:
Most of the administration tasks can be accomplished using
either method; however, some tasks can only be accomplished using one or
the other method.
For example, setting configurations for the ConText Linguistics
can only be enabled for a database session through the command-line, while
custom setting configurations can only be created/modified in the administration
tool. As a result, if you want to use custom settings for the Linguistics,
you must use both the administration tool and the command-line to
administer ConText.
Command-line administration includes:
For example, the command-line for the server machine on which
ConText is installed must be used to start ConText servers and access the
administration utilities provided with ConText.
All remaining ConText administration tasks, such as shutting
down ConText servers, managing queues, and creating indexes, can be performed
using SQL or PL/SQL, either on the server machine or on any other machine
that has SQL*Plus and PL/SQL installed and is connected to the server machine
through SQL*Net.
ConText provides two GUI tools for administering ConText:
Both administration tools are distributed with the ConText
Workbench, which can be installed on any PC running a Microsoft Windows
32-bit environment, such as Windows NT or 95.
| See
Also:
For more information about the GUI administration tools and the other components in the ConText Workbench, see Oracle8 ConText Cartridge Workbench User's Guide. |
The System Administration tool is a client-based application
that provides a 32-bit Windows, graphical user interface (GUI) for administering
ConText servers, text, and the Linguistics from a 32-bit Windows environment,
such as Windows NT or Windows 95.
| See
Also:
For more information about using the System Administration tool, see the online help provided with the tool. |
The Configuration Manager is a Web-based application that
allows the CTXSYS user to manage various administration tasks quickly and
easily. It also incorporates a simple ad-hoc query tool and a utility for
generating Web-based prototype ConText applications.
In contrast to the System Administration tool, which is for
Windows NT and Windows 95 only and is installed separately on each client
machine, the Configuration Manager is platform-independent and is installed
only once per database. Each Configuration Manager installation runs under
the CTXSYS user.
| See
Also:
For more information about using the Configuration Manager, see the online help provided with the tool. |