Release 8.0.5 for Windows NT and Windows 95/98
A64419-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Net8
Getting Started
Release 8.0.5 for Windows NT and Windows 95/98 A64419-01 |
|
This chapter discusses some common network administration
tasks that may need to be performed on the server and client.
Specific topics discussed are:
Common administration tasks to perform on the Oracle Names Server include:
If you are using Oracle Names, start an Oracle Names Server
on the machine where Oracle Names Server is installed and configured with
the NAMESCTL80 control utility or the Control Panel:
Stop an Oracle Names Server (if you are using it) when you
have completed database connections.
Common administration tasks to perform on the server side include:
The following table explains how to start the network listener
using either the control utility LSNRCTL80 or the Windows NT Control Panel:
Stop the network listener when all database connections have
completed, and the Oracle Names Server has been stopped.
Common administration tasks to perform on the Oracle Connection Manager machine include:
|
Note: Start Oracle Names (if you are using it) and the network listener before starting Oracle Connection Manager. |
The table below explains how to start an Oracle Connection
Manager using either the command line utility CMCTL80 or the Windows NT
Control Panel.
Stop the Oracle Connection Manager when the Oracle Names
Server and network listener have been stopped:
After testing the server side configuration, perform client side administration tasks by:
If you are using Oracle Names, you may enable client caching
on clients with the NAMESCTL80 control utility or the Control Panel (for
Windows NT only). Client caching will update the SDNS.ORA file with the
new Oracle Names Server information. If you do not want to update the SDNS.ORA
file, it is not necessary to start this service.
To specify the type of names resolution you want to use:
The profile details appear on the right side of the page.
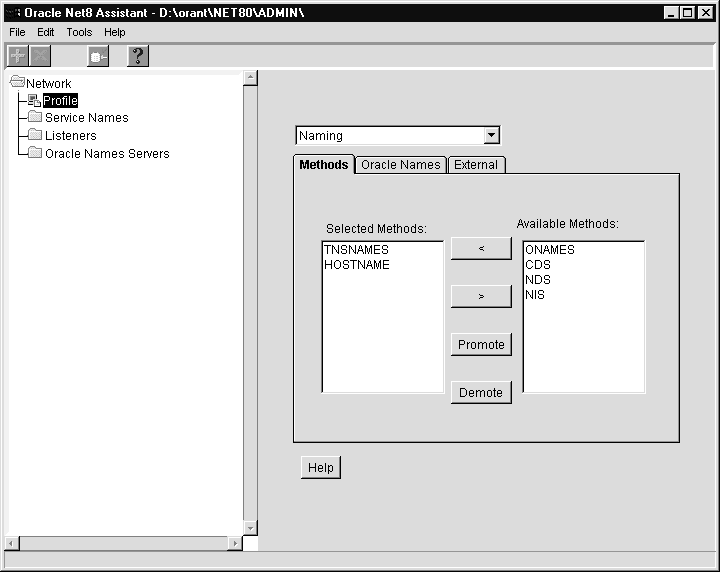
| Naming Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
ONAMES |
Service names are resolved centrally, through a Names Server. You may need to set a Preferred Names Server (using the Oracle Net8 Assistant). See the Oracle Net8 Assistant online help for more information. See "Using the Oracle Names Method" in Chapter 6, "Configuring the Network". |
|
TNSNAMES |
Service names are resolved using the TNSNAMES.ORA file which resides on the client. See "Using the Local Naming Method" in Chapter 6, "Configuring the Network" |
|
HOSTNAME |
Service names are resolved using the Host Naming Adapter. Certain criteria must be met to use host naming names resolution. See "Using the Host Naming Method" in Chapter 6, "Configuring the Network" |
|
CDS |
This naming method is available with the Advanced Networking Option (ANO). See Chapter 7, "Connecting To a Database" and Oracle Advanced Networking Option Administrator's Guide. |
|
NDS |
NetWare Directory Services (NDS) |
If you configured the network using the local naming method, you may:
These changes are saved to the TNSNAMES.ORA file.
To modify a service name:
Oracle Service Name Wizard page displays.
The final window appears.
Oracle Net8 Easy Config modifies the service name in the TNSNAMES.ORA located in ORACLE_HOME\NET80\ADMIN.
To delete a protocol address from a service name in the TNSNAMES.ORA file:
The Oracle Net8 Assistant displays.
The TNSNAMES.ORA file is re-created.
The Oracle Net8 Assistant application exits.
To delete a service name from the TNSNAMES.ORA file:
Oracle Service Name Wizard page displays.
A message appears asking you to confirm your decision to delete the service name.
The final page appears.
If you click Finish, the service name is deleted, and the TNSNAMES.ORA file is re-created.
If you configured the network using the local naming method,
you can add an address to an existing service name.
To add an additional protocol address for a service name:
Oracle Net8 Assistant appears.
The TNSNAMES.ORA file is re-created.
The Oracle Net8 Assistant application exits.
|
Note: The trace facility uses a large amount of disk space and may have a significant impact upon system performance. Therefore, you should enable tracing only when necessary. |
The trace facility produces a detailed sequence of statements
that describe network events as they are executed. Tracing an operation
allows you to obtain more information on the internal operations of the
components of Net8 than is provided in a log file. This information is
output to files that can be evaluated to identify the events that led to
an error.
Tracing assists you in diagnosing and troubleshooting networking performance and problems. Components that can be traced using the trace facility are:
Default trace file names are:
Tracing is enabled by:
The Oracle8 Net8 Assistant can be used to enable:
The Oracle8 Net8 Assistant enables tracing for client and/or
server by setting parameters in the SQLNET.ORA file. When Net8 is run,
SQLNET.TRC is created in ORACLE_HOME\NET80\TRACE.
To enable SQLNET.ORA tracing for a particular client or server:
The profile details appear on the right side of the screen.
The fields for tracing display:
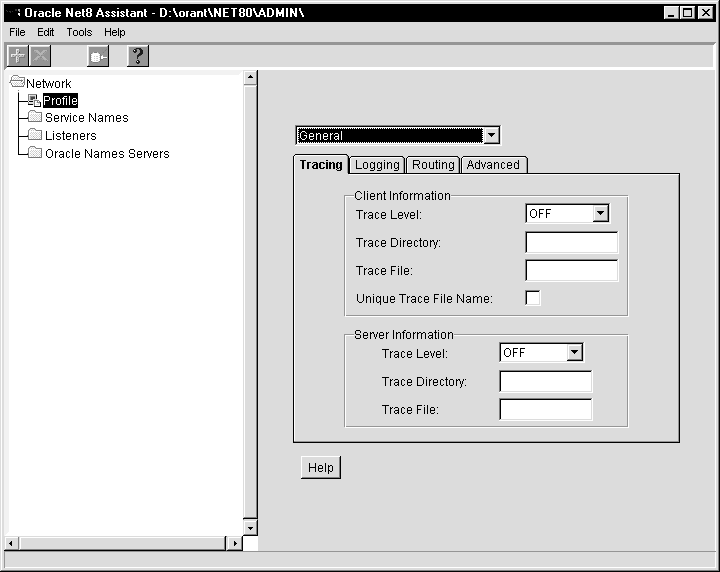
The Oracle Net8 Assistant application exits.
The Oracle8 Net8 Assistant enables tracing for client and/or
server by setting parameters in the SQLNET.ORA file. When Net8 is run,
LISTENER.TRC is created in ORACLE_HOME\NET80\TRACE.
To enable LISTENER.ORA tracing:
The available network listeners display.
The network listener details appear on the right side of the screen.
The fields for logging and tracing display:
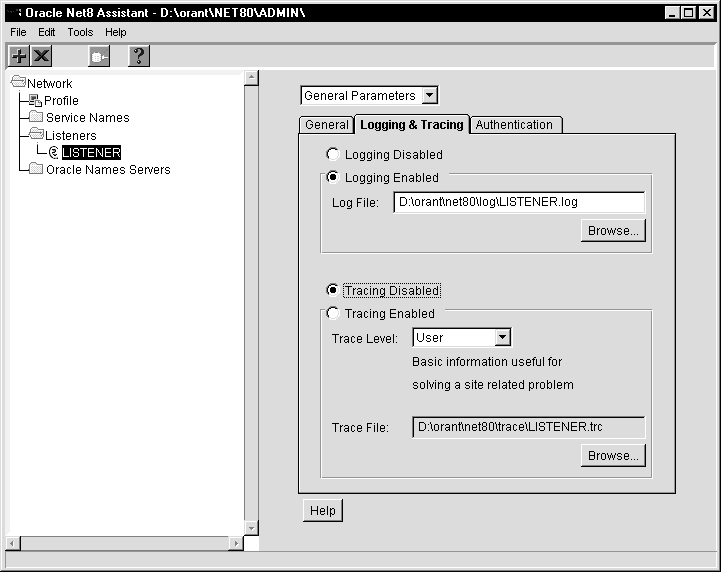
The Oracle Net8 Assistant application exits.
To set SQLNET.ORA and LISTENER.ORA tracing parameters using component configuration files:
To set trace parameters using component control utilities:
Use Trace Assistant to interpret your *.TRC files.
Follow the instructions in section "10.4.3 Using the Trace
Assistant to Examine Your Trace Files", in the Oracle
Net8 Administrator's Guide to run the Trace Assistant.