

 
|
Displays a brief message, an icon, and some buttons. More...
#include <qmessagebox.h>
Inherits QDialog.
| Type | Name | READ | WRITE | Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QString | text | text | setText | |
| Icon | icon | icon | setIcon | |
| QPixmap | iconPixmap | iconPixmap | setIconPixmap | |
| TextFormat | textFormat | textFormat | setTextFormat |
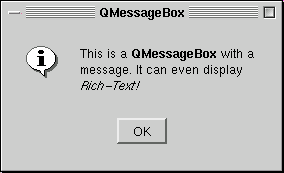
A message box is a modal dialog that displays an icon, a text and up to three push buttons. It's used for simple messages and questions.
QMessageBox provides a range of different messages, arranged roughly along two axes: Severity and complexity.
Severity is
Information - for message boxes that are part of normal operation
Warning - for message boxes that tell the user about unusual errors
Critical - as Warning, but for critical errors
The message box has a different icon for each of the severity levels.
Complexity is one button (Ok) for a simple messages, or two or even three buttons for questions.
There are static functions that let you do most of the common jobs, for example:
If a program is unable to find a supporting file, but can do perfectly well without:
QMessageBox::information( this, "Application name",
"Unable to find the user preferences file.\n"
"The factory default will be used instead." );
warning() can be used to tell the user about unusual errors, or errors which can't be easily fixed:
switch( QMessageBox::warning( this, "Application name",
"Could not connect to the <mumble> server.\n"
"This program can't function correctly "
"without the server.\n\n",
"Try again", "Quit", 0,
0, 1 );
case 0: // Try again or Enter
// try again
break;
case 1: // Quit or Escape
// exit
break;
}
Finally,
The text part of all message box messages can be either rich text or plain text. If you specify a rich text formatted string, it will be rendered using the default stylesheet. See QStyleSheet::defaultSheet() for details. With certain strings that contain XML meta characters, the auto-rich text detection may fail, interpreting plain text falsely as rich text. In these rare cases, use QStyleSheet::convertFromPlainText() to convert your plain text string to a visually equivalent rich text string or set the text format explicitly with setTextFormat().
Here are some examples of how to use the static member functions. After these examples you will find an overview of the non-static member functions.
If a program is unable to find a supporting file, it may perhaps do:
QMessageBox::information( this, "Application name here",
"Unable to find the file \"index.html\".\n"
"The factory default will be used instead." );
The Microsoft Windows User Interface Guidelines strongly recommends using the application name as window caption. The message box has just one button, OK, and its text tells the user both what happened and what the program will do about it. Since the application is able to make do, the message box is just information, not a warning or a critical error.
Exiting a program is part of its normal operation, and if there are unsaved data the user probably should be asked what to do, for example like this:
switch( QMessageBox::information( this, "Application name here",
"The document contains unsaved work\n"
"Do you want to save it before exiting?",
"&Save", "&Don't Save", "&Cancel",
0, // Enter == button 0
2 ) ) { // Escape == button 2
case 0: // Save clicked, Alt-S or Enter pressed.
// save
break;
case 1: // Don't Save clicked or Alt-D pressed
// don't save but exit
break;
case 2: // Cancel clicked, Alt-C or Escape pressed
// don't exit
break;
}
Again, the application name is used as window caption, as Microsoft recommends. The Escape button cancels the entire Exit operation, and Enter/Return saves the document and exits.
Disk full errors are unusual (in a perfect world, they are) and they certainly can be hard to correct. This example uses predefined buttons instead of hardcoded button texts:
switch( QMessageBox::warning( this, "Application name here",
"Could not save the the user preferences,\n"
"because the disk is full. You can delete\n"
"some files and press Retry, or you can\n"
"abort the Save Preferences operation.",
QMessageBox::Retry | QMessageBox::Default,
QMessageBox::Abort | QMessageBox::Escape )) {
case QMessageBox::Retry: // Retry or Enter
// try again
break;
case QMessageBox::Abort: // Abort or Cancel
// abort
break;
}
The critical() function should be reserved for critical errors. In this example, errorDetails is a QString or const char*, and QString is used to concatenate several strings:
QMessageBox::critical( 0, "Application name here",
QString("An internal error occurred. Please ") +
"call technical support at 123456789 and report\n"+
"these numbers:\n\n" + errorDetails +
"\n\n<Application> will now exit." );
QMessageBox provides a very simple About box, which displays an appropriate icon and the string you give it:
QMessageBox::about( this, "About <Application>",
"<Application> is a <one-paragraph blurb>\n\n"
"Copyright 1951-1997 Such-and-such. "
"<License words here.>\n\n"
"For technical support, call 123456789 or see\n"
"http://www.such-and-such.com/Application/\n" );
See about() for more information.
Finally, you can make a QMessageBox from scratch and set custom button texts:
QMessageBox mb( "Application name here",
"Saving the file will overwrite the old file on disk.\n"
"Do you really want to save?",
QMessageBox::Information,
QMessageBox::Yes | QMessageBox::Default,
QMessageBox::No,
QMessageBox::Cancel | QMessageBox::Escape );
mb.setButtonText( QMessageBox::Yes, "Save" );
mb.setButtonText( QMessageBox::No, "Don't Save" );
switch( mb.exec() ) {
case QMessageBox::Yes:
// save and exit
break;
case QMessageBox::No:
// exit without saving
break;
case QMessageBox::Cancel:
// don't save and don't exit
break;
}
QMessageBox defines two enum types, Icon and an unnamed button type.
Icon defines the Information, Warning and Critical icons for
each GUI style. It is used by the constructor, by the static member
functions information(), warning() and critical(), and there is a
function called standardIcon() which gives you access to the various
icons.
The button types are:
Ok - the default for single-button message boxes
Cancel - note that this is not automatically Escape
Yes
No
Abort
Retry
Ignore
Button types can be combined with two modifiers by using OR:
Default - makes pressing Enter or Return be equivalent with
clicking this button. Normally used with Ok, Yes or similar.
Escape - makes pressing Escape be equivalent with this button.
Normally used with Abort, Cancel or similar.
The text(), icon() and iconPixmap() functions provide access to the current text and pixmap of a message box, and setText(), setIcon() and setIconPixmap() lets you change it. The difference between setIcon() and setIconPixmap() is that the former accepts a QMessageBox::Icon and can it be used to set standard icons while the latter accepts a QPixmap and can be used to set custom icons.
setButtonText() and buttonText() provide access to the buttons.
QMessageBox has no signals or slots.
See also QDialog, Isys on error messages, and GUI Design Handbook: Message Box.
QMessageBox::NoIcon
QMessageBox::Information
QMessageBox::Warning
QMessageBox::Critical
Constructs a message box with no text and a button with the text "OK".
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
The parent and name arguments are passed to the QDialog constructor.
Constructs a message box with a caption, a text, an icon and up to three buttons.
The icon must be one of:
QMessageBox::NoIcon
QMessageBox::Information
QMessageBox::Warning
QMessageBox::Critical
Each button can have one of the following values:
QMessageBox::NoButton
QMessageBox::Ok
QMessageBox::Cancel
QMessageBox::Yes
QMessageBox::No
QMessageBox::Abort
QMessageBox::Retry
QMessageBox::Ignore
Use QMessageBox::NoButton for the later parameters to have less than three buttons in your message box.
One of the buttons can be combined with the QMessageBox::Default flag
to make a default button.
One of the buttons can be combined with the QMessageBox::Escape flag
to make an escape option. Hitting the Esc key on the keyboard has
the same effect as clicking this button with the mouse.
Example:
QMessageBox mb( "Hardware failure",
"Disk error detected\nDo you want to stop?",
QMessageBox::NoIcon,
QMessageBox::Yes | QMessageBox::Default,
QMessageBox::No | QMessageBox::Escape );
if ( mb.exec() == QMessageBox::No )
// try again
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
If modal is TRUE the message becomes modal, otherwise it becomes modeless.
The parent, name, modal and f arguments are passed to the QDialog constructor.
See also setCaption(), setText() and setIcon().
Destructs the message box.
[static]Displays a simple about box with window caption caption and body text text.
about() looks for a suitable icon for the box in four locations:
The about box has a single button labelled OK.
See also QWidget::icon() and QApplication::mainWidget().
Examples: menu/menu.cpp
[static]Displays a simple message box about Qt, with window caption caption and optionally centered over parent. The message includes the version number of Qt being used by the application.
This is neat for inclusion into the Help menu. See the menu.cpp example.
Examples: menu/menu.cpp trivial/trivial.cpp
[virtual]Adjusts the size of the message box to fit the contents just before QDialog::exec() or QDialog::show() is called.
This function will not be called if the message box has been explicitly resized before showing it.
Reimplemented from QWidget.
Returns the text of the message box button button, or null if the message box does not contain the button.
See also setButtonText().
[static]Displays a critical error message box with a caption, a text and 1-3 buttons. Returns the number of the button that was clicked (0, 1 or 2).
button0Text is the text of the first button and is optional. If button0Text is not supplied, "OK" (translated) will be used. button1Text is the text of the second button and is optional, and button2Text is the text of the third button and is optional. defaultbuttonNumber (0-2) is the index of the default button; pressing Return or Enter is the same as clicking the default button. It defaults to 0 (the first button). escapeButtonNumber is the index of the Escape button; pressing Escape is the same as clicking this button. It defaults to -1 (pressing Escape does nothing); supply 0, 1 or 2 to make pressing Escape be equivalent with clicking the relevant button.
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
See also information() and warning().
[static]Opens a critical message box with a caption, a text and up to three buttons. Returns the identifier of the button that was clicked.
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
See also information() and warning().
Returns the icon of the message box.
See also setIcon() and iconPixmap().
Returns the icon pixmap of the message box.
Example:
QMessageBox mb(...);
mb.setIcon( QMessageBox::Warning );
mb.iconPixmap(); // returns the warning icon pixmap
See also setIconPixmap() and icon().
[static]Displays an information message box with a caption, a text and 1-3 buttons. Returns the number of the button that was clicked (0, 1 or 2).
button0Text is the text of the first button and is optional. If button0Text is not supplied, "OK" (translated) will be used. button1Text is the text of the second button and is optional. button2Text is the text of the third button and is optional. defaultbuttonNumber (0-2) is the index of the default button; pressing Return or Enter is the same as clicking the default button. It defaults to 0 (the first button). escapeButtonNumber is the index of the Escape button; pressing Escape is the same as clicking this button. It defaults to -1 (pressing Escape does nothing); supply 0, 1 or 2 to make pressing Escape be equivalent with clicking the relevant button.
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
See also warning() and critical().
Examples: picture/picture.cpp
[static]Opens an information message box with a caption, a text and up to three buttons. Returns the identifier of the button that was clicked.
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
See also warning() and critical().
[virtual protected]Reimplemented for internal reasons; the API is not affected.
Reimplemented from QWidget.
[virtual protected]Reimplemented for internal reasons; the API is not affected.
Reimplemented from QWidget.
Sets the text of the message box button button to text. Setting the text of a button that is not in the message box is quietly ignored.
See also buttonText().
Sets the icon of the message box to icon, which is a predefined icon:
QMessageBox::NoIcon
QMessageBox::Information
QMessageBox::Warning
QMessageBox::Critical
The actual pixmap used for displaying the icon depends on the current GUI style. You can also set a custom pixmap icon using the setIconPixmap() function.
See also icon(), setIconPixmap() and iconPixmap().
[virtual]Reimplemented for internal reasons; the API is not affected.
Reimplemented from QWidget.
Sets the icon of the message box to a custom pixmap. Note that it's often hard to draw one pixmap which looks appropriate in both Motif and Windoes GUI styles. You may want to draw two.
See also iconPixmap() and setIcon().
Sets the message box text to be displayed.
text will be interpreted either as a plain text or as a rich
text, depending on the text format setting; see setTextFormat(). The
default setting is AutoText, i.e. the message box will try to
auto-detect the format of text.
See also text() and setTextFormat().
Sets the text format to format. See the Qt::TextFormat enum for an explanation of the possible options.
The default format is AutoText.
See also textFormat() and setText().
[static]Returns the pixmap used for a standard icon. This allows the pixmaps to be used in more complex message boxes.
[protected]Reimplemented for internal reasons; the API is not affected.
Returns the message box text currently set, or a null string if no text has been set.
See also setText() and textFormat().
Returns the current text format.
See also setTextFormat().
[static]Displays a warning message box with a caption, a text and 1-3 buttons. Returns the number of the button that was clicked (0, 1 or 2).
button0Text is the text of the first button and is optional. If button0Text is not supplied, "OK" (translated) will be used. button1Text is the text of the second button and is optional, and button2Text is the text of the third button and is optional. defaultbuttonNumber (0-2) is the index of the default button; pressing Return or Enter is the same as clicking the default button. It defaults to 0 (the first button). escapeButtonNumber is the index of the Escape button; pressing Escape is the same as clicking this button. It defaults to -1 (pressing Escape does nothing); supply 0, 1 or 2 to make pressing Escape be equivalent with clicking the relevant button.
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
See also information() and critical().
Examples: i18n/main.cpp
[static]Opens a warning message box with a caption, a text and up to three buttons. Returns the identifier of the button that was clicked.
If parent is 0, then the message box becomes an application-global modal dialog box. If parent is a widget, the message box becomes modal relative to parent.
See also information() and critical().
Search the documentation, FAQ, qt-interest archive and more (uses
www.trolltech.com):
This file is part of the Qt toolkit, copyright © 1995-2000 Trolltech, all rights reserved.
| Copyright İ 2000 Trolltech | Trademarks | Qt version 2.2.1
|