| Oracle Network Products Troubleshooting Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Network Products Troubleshooting Guide | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
Note: There may be more than one SQLNET.ORA file available, a system-level and a user-level file. If both are available, the values for the variables in the user-level file take priority over those in the system-level file.
On most machines, start the Client Status Monitor by entering the following at the command line of your client machine:
csm
On clients running MS Windows, start the Client Status Monitor by double-clicking on the Client Status Monitor icon.
The Client Status Monitor can be run in command line mode or with a graphical user interface. There is one graphical user interface available for UNIX workstations and another for machines running MS Windows. These interfaces offer similar functionality, but their organization is slightly different.
The rest of this chapter describes the Client Status Monitor from the point of view of each of the three interfaces:
 Figure 4 - 1. Client Status Monitor - Main Window
Figure 4 - 1. Client Status Monitor - Main Window
Most of the windows display information about your system and are read-only.
 Figure 4 - 2. Identifying Information for Oracle Customer Support
Figure 4 - 2. Identifying Information for Oracle Customer Support
Enter the following information in the appropriate fields.
From
Name of person at your location who is the liaison with Oracle Customer Support
Phone
Phone number of the person at your location who is the liaison with Oracle Customer Support
Fax Number
Fax number of the person at your location who is the liaison with Oracle Customer Support
Customer Support ID
Identifying number that authorizes you to get help from Oracle Customer Support
Subject
Optional field in which to explain the problem
Comment
Optional field for additional information
To save the information in this window, select OK.
To print the Fax Report, which includes the information in this window as well as all the client information from the Client Status Monitor, select Print Report.
To cancel your entries on this window, select Cancel.
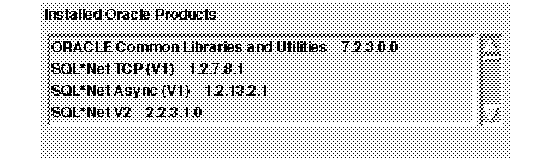 Figure 4 - 3. Installed Products Window
Figure 4 - 3. Installed Products Window
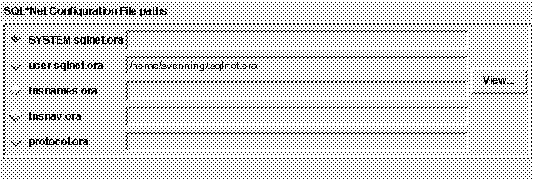 Figure 4 - 4. SQL*Net Configuration Files
Figure 4 - 4. SQL*Net Configuration Files
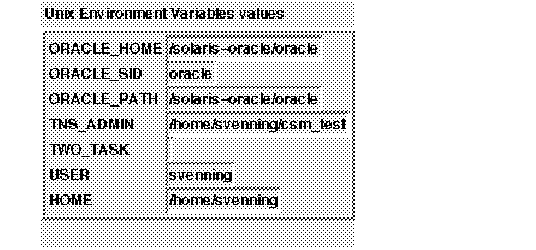 Figure 4 - 5. Environmental Variables
Figure 4 - 5. Environmental Variables
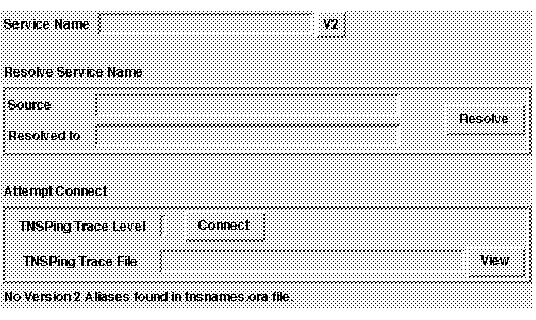 Figure 4 - 6. Resolve Service Name
Figure 4 - 6. Resolve Service Name
To use this window, enter the service name of the database you wish to reach, and select the Resolve button. The names resolution method appears in the Source field, and the address appears in the Resolved To field.
Note: The names resolution method should match the first method shown in the names resolution path field in the Name Resolution Services window.
You can see if a connection is possible to this service by running the TNSPING utility. To do so, select the Connect button. A connection will be attempted.
If you have selected a TNSPING trace level, the connection attempt will be traced. You can view the trace file by selecting the View button.
Note: You cannot turn on tracing and set the TNSPING trace level on this screen. Use the SQLNET.ORA Editor to set the trace level.
If you are missing required files, a message telling you so appears at the bottom of the window. An example of this is shown in Figure 4 - 6.
The SQLNET.ORA files contain parameters that affect the behavior of the client. If created by Oracle Network Manager, the SQLNET.ORA file has values that are the same for all clients of a particular client profile, or client type. Once the SQLNET.ORA files are distributed to individual clients, however, they can be modified to reflect individual needs. The SQLNET.ORA Editor provides a convenient way to do this.
Note: Not all parameters in SQLNET.ORA can be modified using this editor. Specifically, not all parameters related to Authentication in Secure Network Services are available to this tool in this release. Also, you cannot use this tool to set preferred Names Servers.
The main SQLNET.ORA Editor window looks like that shown in Figure 4 - 7.
 Figure 4 - 7. SQLNET.ORA Editor
Figure 4 - 7. SQLNET.ORA Editor
Each of the buttons in the SQLNET.ORA Editor window brings up a window in which you can edit a number of parameters.
Attention: Be careful when using this tool. Many client parameters work in conjunction with server parameters which you cannot see with this tool. Do not change any parameters unless you are sure of the result.
There are three buttons at the bottom of each of the SQLNET.ORA Editor windows.
Client LOG File Name
Client LOG Directory
You can change the existing directory to which the client log file is written in this field. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
Client Registration
Enter an identifier for the client machine. This identifier will be passed to the listener with any connection request and included in the Audit Trail. The identifier can be any alphanumeric string up to 128 characters. A typical identifier might be a department name.
Default Domain
The default domain is the domain to which most client connection requests are directed. In a hierarchical name space, the default domain should be the domain in which the most frequently contacted servers reside.
You can toggle the following features ON and OFF by selecting the buttons next to their names.
Automatic IPC
Select this button if you want the client to try an IPC (internal) connection before trying other protocols. The default is for Automatic IPC to be ON.
Select this button if you want to make a connection to a dedicated server rather than to use a multi-threaded server.
DISABLE Out of Band Breaks (OOB)
Select this button if you want to disable out-of-band breaks.
For further information about these optional parameters, refer to the appropriate sections in Understanding SQL*Net.
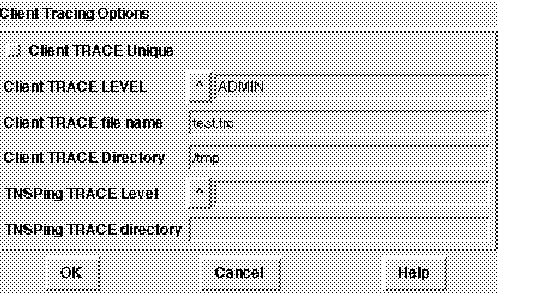 Figure 4 - 8. Tracing Parameters
Figure 4 - 8. Tracing Parameters
Client Trace Level
Select a trace level from the scrolling list. Unless you are troubleshooting a particular problem, the trace level should be OFF. Other choices are USER, for a moderately detailed trace report, and ADMIN, for more extensive trace information.
Note: After troubleshooting your connection problem, turn trace level back to OFF. Leaving the trace facility on can impact performance.
Client Trace File Name
Change the existing name for the trace file in this field. In most operating systems, the trace filename is automatically appended with the suffix .TRC. You do not need to enter that suffix in the field.
Client Trace Directory
Change the existing directory to which the client trace file is written in this field. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
TNSPING Trace Level
Trace the behavior of the TNSPING utility by selecting a trace level from the scrolling list. Unless you are troubleshooting a particular problem, the trace level should be OFF. Other choices are USER, for a moderately detailed trace report, and ADMIN, for more extensive trace information.
Note: After troubleshooting your connection problem, turn trace level back to OFF. Leaving the trace facility on can impact performance.
TNSPING Trace Directory
Override the default location of the TNSPING trace file using this field. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
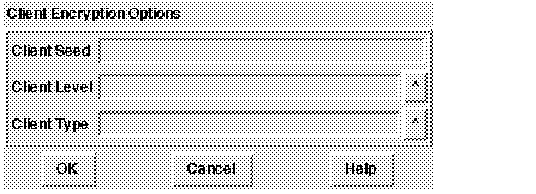 Figure 4 - 9. Client Encryption Parameters
Figure 4 - 9. Client Encryption Parameters
Client Seed
Enter a new random number to act as a seed for encryption of client messages in this field. Enter a string of between 16 and 70 random characters.
Client Level
Change the level of encryption the client requests using this field. Choices in the pop-up list are Accepted, Rejected, Requested, and Required. (Whether encryption is implemented in a client-server connection is determined by the level requested by both the client and the server.)
Client Type
Select the type of encryption from the choices available in the pop-up list. (Do not select a type unless it has been installed. Even if a type appears in the list, it may not be installed in your system.)
S
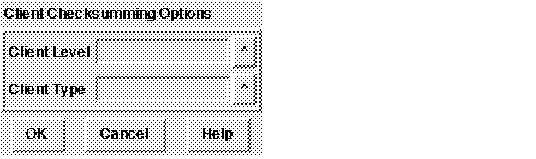 Figure 4 - 10. Client Checksum Parameters
Figure 4 - 10. Client Checksum Parameters
Client Level
Choose the client's requested level of checksumming from the pop-up list. Choices are Accepted, Rejected, Requested, and Required. (Whether checksumming is implemented in a client-server connection is determined by the level requested by both the client and the server.)
Client Type
Select the type of checksumming from the choices available in the pop-up list. In this release, only MD5 is available. (Do not select a type unless it has been installed.)
 Figure 4 - 11. Client Authentication Parameter
Figure 4 - 11. Client Authentication Parameter
Note: If you select CYBERSAFE or KERBEROS5, you may need to modify other parameters that are not accessible from the SQLNET.ORA Editor. Both these authentication adapters require other parameters to be set. If they are not already set in the SQLNET.ORA file, you must set them through Oracle Network Manager, or by using a text editor.
 Figure 4 - 12. Name Resolution Parameter
Figure 4 - 12. Name Resolution Parameter
Note: These windows are read-only. To change any of the values, use the SQLNET.ORA Editor.
 Figure 4 - 13. General Client Properties
Figure 4 - 13. General Client Properties
To view any of the files listed in this window, select the file and select View. A scrollable window displaying the file appears. To print the file, select Print from the display window.
 Figure 4 - 14. Oracle Protocol Adapters
Figure 4 - 14. Oracle Protocol Adapters
 Figure 4 - 15. Checksumming Services
Figure 4 - 15. Checksumming Services
The fields in this window display the following information:
 Figure 4 - 16. Client Encryption Parameters
Figure 4 - 16. Client Encryption Parameters
 Figure 4 - 17. Client Authentication
Figure 4 - 17. Client Authentication
 Figure 4 - 18. Name Resolution Services
Figure 4 - 18. Name Resolution Services
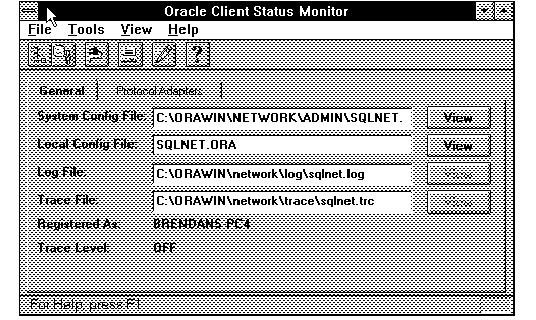 Figure 4 - 19. Initial Client Status Monitor Window
Figure 4 - 19. Initial Client Status Monitor Window
This window includes a menu bar from which you can access other windows, as described in the following section, and a page that displays the names and paths to important client files.
Note: You can choose whether or not to display the icons by selecting Toolbar from the View menu.
 Figure 4 - 20. Toolbar
Figure 4 - 20. Toolbar
The icons and their functions are as follows:
Show/Hide SNS Pages
Equivalent to selecting Secure Network Services Details from the View menu
Show/Hide Naming page
Equivalent to selecting Native Naming Details from the View menu
Test Connection
Equivalent to selecting Test Connection from the Tools menu
Generate Report
Equivalent to selecting Generate Report from the File menu
SQLNET.ORA Editor
Equivalent to selecting SQLNET.ORA Editor from the Tools menu
Help
Equivalent to selecting Index from the Help menu
The following sections describe the Test Connection, Generate Report, and SQLNET.ORA Editor options in detail.
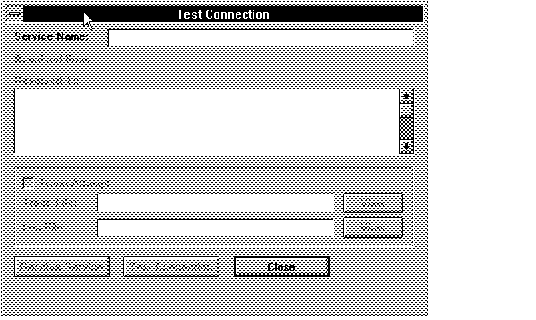 Figure 4 - 21. Test Connection Window
Figure 4 - 21. Test Connection Window
To use this window, enter the service name of the database you wish to reach, and select Resolve Service. The names resolution method will appear in the Resolved From field, and the address will appear in the Resolved To field.
Note: The names resolution method should match the first one shown in the names resolution path field in the Name Resolution Services window.
You can see if a connection is possible to this service by selecting Test Connection. If you select Trace Attempt you can view the trace file that results.
Note: You cannot turn on tracing and set the trace level from this window. Use the SQLNET.ORA Editor to set the trace level.
If a trace and log file are created, you can view them by selecting View, and you can print them from the Viewer window.
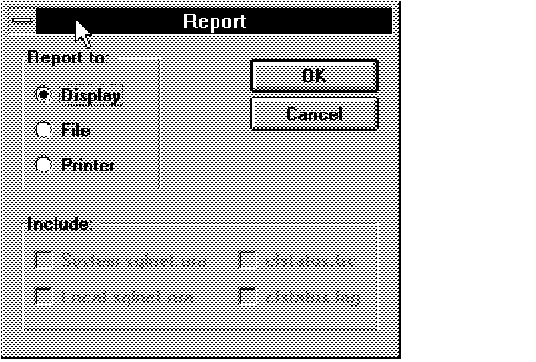 Figure 4 - 23. Report Window
Figure 4 - 23. Report Window
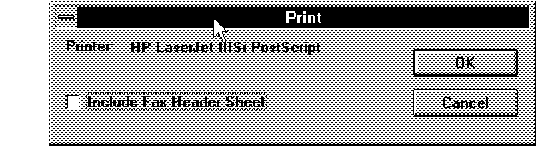 Figure 4 - 24. Initial Print Page
Figure 4 - 24. Initial Print Page
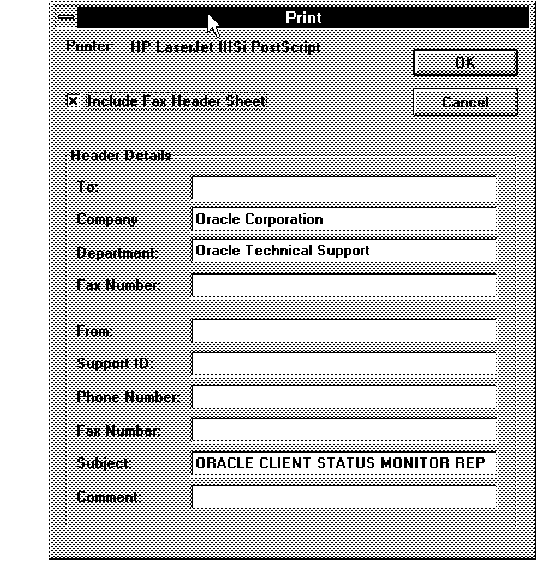 Figure 4 - 25. Print with Fax Header Sheet
Figure 4 - 25. Print with Fax Header SheetEnter the following information in the appropriate empty fields.
To
Person to contact within Oracle Customer Support, if known
Fax Number
Fax number of the branch of Oracle Customer Support for your area
From
Name of person at your location who is the liaison with Oracle Customer Support
Support ID
Identifying number that authorizes you to get help from Oracle Customer Support
Phone Number
Phone number of the person at your location who is the liaison with Oracle Customer Support
Fax Number
Fax number of the person at your location who is the liaison with Oracle Customer Support
Comment
Optional field in which to explain the problem
To print the report, which includes the information in this window as well as all the client information from the Client Status Monitor, select OK.
To close this window, select Cancel.
You can open the SQLNET.ORA Editor on an MS Windows machine directly by double-clicking in the SQLNET.ORA Editor icon. You can also access the SQLNET.ORA Editor from the Client Status Monitor. Either way, when you open the SQLNET.ORA Editor you are asked whether you want to edit the system level SQLNET.ORA file, the local (user level) SQLNET.ORA file, or another SQLNET.ORA file. If you select Other, a window appears in which you select the location of the file you want to edit.
Values in the local (user) SQLNET.ORA file override those in the system SQLNET.ORA file.
Note: You might not have write permission for the system SQLNET.ORA file.
Note: Not all parameters in SQLNET.ORA can be modified using this editor. Specifically, not all parameters related to Authentication in Secure Network Services are available to this tool in this release. Also, you cannot use this tool to set preferred Names Servers.
Like the Client Status Monitor, the SQLNET.ORA Editor has a number of pages, which are displayed when you select their folder tabs.
There are four buttons at the bottom of the SQLNET.ORA Editor window:
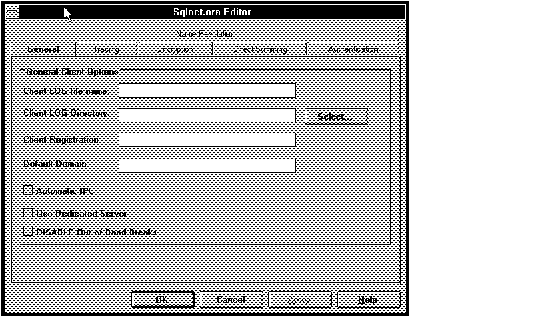 Figure 4 - 26. SQLNET.ORA Editor General Page
Figure 4 - 26. SQLNET.ORA Editor General Page
Client LOG File Name
Client LOG Directory
Client Registration
Enter an identifier for the client machine. This identifier will be passed to the listener with any connection request and included in the Audit Trail. The identifier can be any alphanumeric string up to 128 characters. A typical identifier might be a department name.
Default Domain
You can toggle the following features ON and OFF by selecting the buttons next to their names.
Automatic IPC
Use Dedicated Server
DISABLE Out of Band Breaks (OOB)
Select this button if you want to disable out-of-band breaks.
For further information about these optional parameters, please refer to the appropriate sections in Understanding SQL*Net.
Press OK to apply your changes; press Cancel to cancel them.
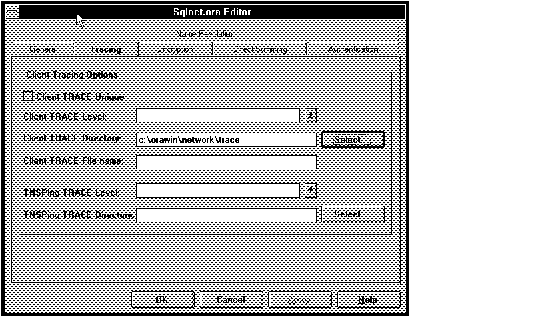 Figure 4 - 27. SQLNET.ORA Editor Tracing Page
Figure 4 - 27. SQLNET.ORA Editor Tracing Page
Client Trace Unique
Select this box to toggle the value of this parameter to ON. When set to ON, this parameter will give each client trace file a different identifying number so that repeated traces do not overwrite one another.
Client Trace Level
Select a trace level from the scrolling list. Unless you are troubleshooting a particular problem, the trace level should be OFF. Other choices are USER, for a moderately detailed trace report, and ADMIN, for more extensive trace information.
NOTE: After troubleshooting your connection problem, turn trace level back to OFF. Leaving the trace facility on can impact performance.
Client Trace File Name
Change the existing name for the trace file in this field. In most operating systems, the trace file name is automatically appended with the suffix .TRC. You do not need to enter that suffix in the field.
Client Trace Directory
Change the existing directory to which the client trace file is written in this field. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
TNSPING Trace Level
Ttrace the behavior of the TNSPING utility by selecting a trace level from the scrolling list. Unless you are troubleshooting a particular problem, the trace level should be OFF. Other choices are USER, for a moderately detailed trace report, and ADMIN, for more extensive trace information.
Note: After troubleshooting your connection problem, turn trace level back to OFF. Leaving the trace facility ON can impact performance.
TNSPING Trace Directory
Change the location of the TNSPING trace file from the platform-specific default by entering the desired location in this field. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
Press OK to apply your changes; press Cancel to cancel them.
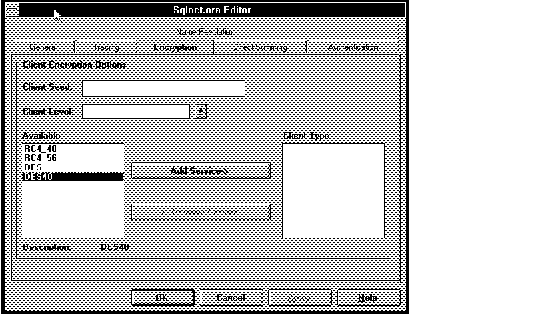 Figure 4 - 28. SQLNET.ORA Editor Encryption Page
Figure 4 - 28. SQLNET.ORA Editor Encryption Page
Client Seed
Enter a new random number to act as a seed for encryption of client messages. Enter a string of between 16 and 70 random characters.
Client Level
Change the level of encryption the client requests. Choices in the pop-up list are Accepted, Rejected, Requested, and Required. (Whether encryption is implemented in a client-server connection is determined by the level requested by both the client and the server.)
Client Type
Select the type of encryption desired from the choices in the Available list box on the left. (Do not select a type unless it has been installed. Even if a type appears in the list, it may not be installed in your system.) You can select more than one type. Remove a type from the Client Type list box by selecting it and selecting Remove.
Press OK to apply your changes; press Cancel to cancel them.
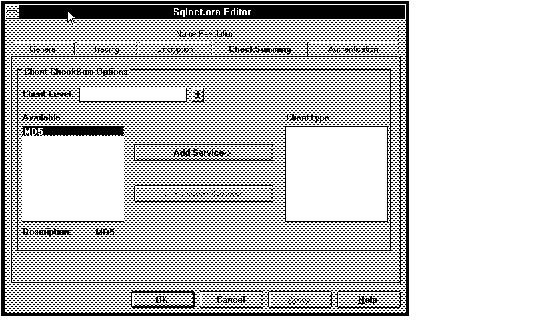 Figure 4 - 29. SQLNET.ORA Editor Checksumming Page
Figure 4 - 29. SQLNET.ORA Editor Checksumming Page
Client Level
Change the client's requested level of checksumming. Choices in the pop-up list are Accepted, Rejected, Requested, and Required. (Whether checksumming is implemented in a client-server connection is determined by the level requested by both the client and the server.)
Client Type
Select the type of checksumming from the choices available in the Available list box. In this release, only MD5 is available. (Do not select a type unless it has been installed.)
Press OK to apply your changes; press Cancel to cancel them.
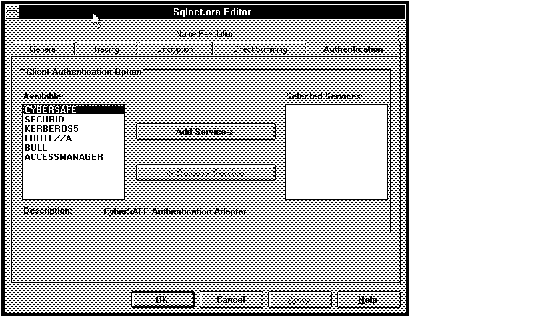 Figure 4 - 30. SQLNET.ORA Editor Authentication Page
Figure 4 - 30. SQLNET.ORA Editor Authentication Page
Note: If you select CYBERSAFE or KERBEROS5, you may need to modify other parameters that are not accessible from the SQLNET.ORA Editor. Both these authentication adapters require other parameters to be set. If they are not already set in the SQLNET.ORA file, you must set them through Oracle Network Manager, or by using a text editor. See Secure Network Services Administrator's Guide and your Oracle platform-specific documentation for more information.
Press OK to apply your changes; press Cancel to cancel them.
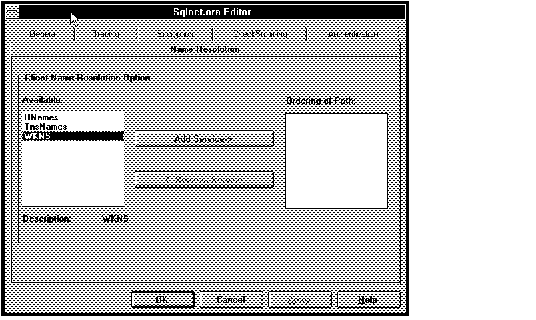 Figure 4 - 31. SQLNET.ORA Editor Name Resolution Page
Figure 4 - 31. SQLNET.ORA Editor Name Resolution Page
To change the order of the names services selected in the Ordering of Names list box, select the service at the top of the list and select Remove, then select it from the Available list and select Add. It will reappear in the Ordering of Path list at the bottom.
Press OK to apply your changes; press Cancel to cancel them.
The default, if no selections are made, is for TNSNAMES to be tried first.
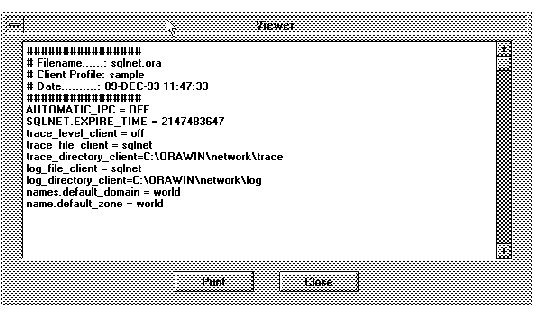 Figure 4 - 32. Viewer Window for a SQLNET.ORA File
Figure 4 - 32. Viewer Window for a SQLNET.ORA File
The General page also shows any client registration information that appears in the SQLNET.ORA file, and shows the current trace level.
Note: The trace level and client registration shown on the General page are those in the local (user) SQLNET.ORA file, if one is available. The values in the local SQLNET.ORA file override the values in the system SQLNET.ORA file.
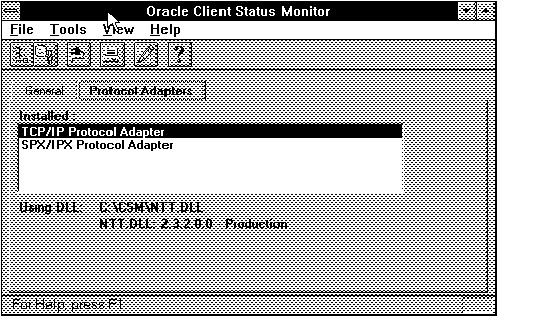 Figure 4 - 33. Protocol Adapter Page
Figure 4 - 33. Protocol Adapter Page
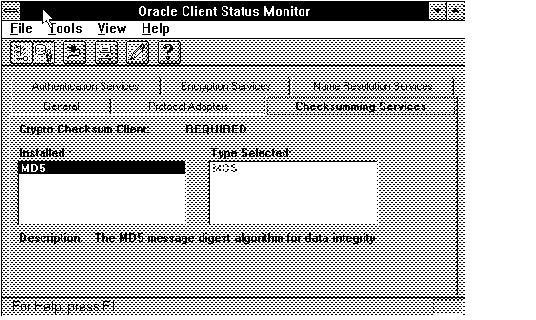 Figure 4 - 34. Checksumming Page
Figure 4 - 34. Checksumming Page
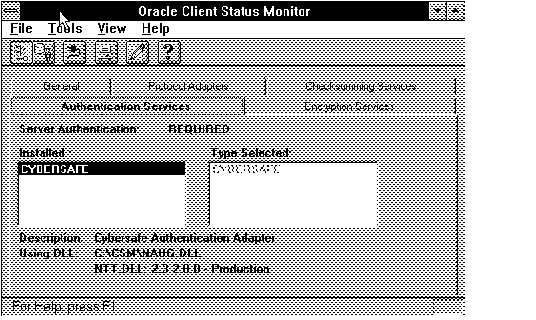 Figure 4 - 35. Authentication Page
Figure 4 - 35. Authentication Page
The highlighted service is described briefly, and the DLL used by the highlighted service is displayed.
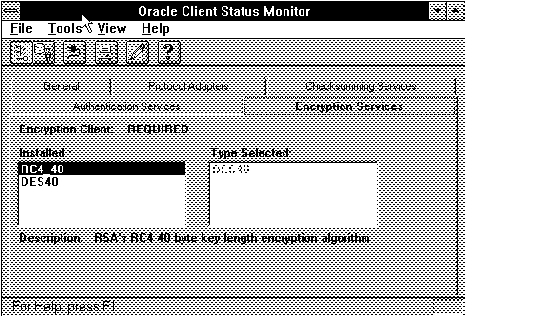 Figure 4 - 36. Encryption Page
Figure 4 - 36. Encryption Page
The highlighted service is described briefly in the Description area.
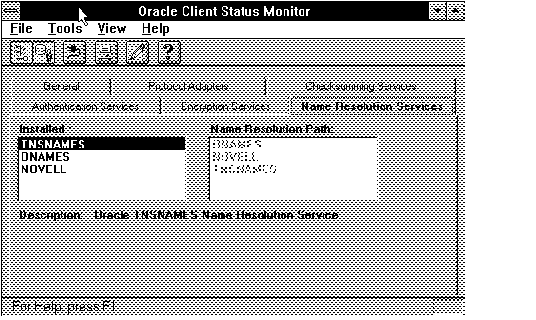 Figure 4 - 37. Name Resolution Page
Figure 4 - 37. Name Resolution Page
The highlighted service is described in the Description area.
Note: Command line mode is not appropriate to use on machines running MS Windows. Use the graphical interface for Windows, described earlier.
status monitor> help
The following display appears:
SHOW ALL SHOW NAME_RESOLUTION_SERVICES SHOW GENERAL SHOW INSTALLED_PRODUCTS SHOW NETWORK_PROTOCOL_ADAPTERS SHOW CSI_INFORMATION SHOW SYSTEM_SQLNET_OPTIONS SHOW SECURE_NETWORK_SERVICES SHOW FILE_PATHS SHOW USER_SQLNET_OPTIONS SHOW UNIXENV SHOW MAN_PAGE SET USE_DEDICATED_SERVER SET TRACE_DIRECTORY_CLIENT SET DISABLE_OOB SET TRACE_FILE_CLIENT SET SQLNET.CLIENT_REGISTRATION SET AUTOMATIC_IPC SET TNSPING.TRACE_LEVEL SET TNSPING.TRACE_DIRECTORY SET TRACE_LEVEL_CLIENT SET CSI_ID SET CSI_PHONE SET CSI_FAX SET CSI_FROM SET CSI_SUBJECT SET CSI_COMMENT RESOLVE_SERVICE_NAME ATTEMPT_CONNECT PRINT_REPORT HELP QUIT
These commands enable you to show or set the same information as you can using the graphical version of the tool.
Note: Within the Client Status Monitor, case is not significant. For example, you can enter either HELP or help.
For example, if you want to display the general information for your client, enter the following:
Status Monitor> SHOW GENERAL
A display like the following appears on your screen:
*** General *** TNS for Unix: Version 2.1.6.1.0 Production system config file => user config file => log file => /home/jshaw/sqlnet.log client trace file => registration => client tracelevel => OFF
To set parameters, enter the value you wish to set following the command name.
For example, to set the name of the contact for Oracle Customer Support to be JShaw, enter the following:
Status Monitor> SET CSI_CONTACT JSHAW
If you want to edit the SQLNET.ORA file to turn tracing ON, enter the following:
Status Monitor> SET TRACE_LEVEL_CLIENT ADMIN
> CSM SHOW GENERAL
After the Client Status Monitor has carried out the command, the operating system prompt returns.
Status Monitor> SHOW INSTALLED_PRODUCTS
The Client Status Monitor displays a list of all the Oracle products on this machine.
Status Monitor> SHOW FILE_PATHS
The Client Status Monitor displays the paths of the SQL*Net configuration files on the client machine.
Status Monitor> SHOW UNIXENV
The Client Status Monitor displays the environment variables for your operating system.
Status Monitor> SHOW NAME_RESOLUTION_SERVICES
The Client Status Monitor displays the name resolution services available to the client, and shows the order in which they are used.
Status Monitor> SHOW NETWORK_PROTOCOL_ADAPTERS
The Client Status Monitor displays the protocol adapters installed on the client.
Status Monitor> SHOW SECURE_NETWORK_SERVICES
The Client Status Monitor displays the security services available to the client. These services include encryption, checksumming, and authentication.
Status Monitor> SHOW ALL
The Client Status Monitor displays all the the information available through the individual commands listed in this section.
Status Monitor> SET CSI_ID customer_ID
Status Monitor> SET CSI_PHONE phone_number_of_local_contact
Status Monitor> SET CSI_FAX fax_number_of_local_contact
Status Monitor> SET CSI_CONTACT name_of_local_contact
After providing the identifying information, print the fax page by entering the following command:
Status Monitor> PRINT_FAXPAGE
Status Monitor> SET USE_DEDICATED_SERVER ON|OFF
Use this command to make a connection to a dedicated server rather than to use a multi-threaded server.
Status Monitor> SET DISABLE_OOB ON|OFF
Use this command to disable (or enable) out-of-band breaks. The default is for out-of-band breaks to be enabled.
Status Monitor> SET TRACE_LEVEL_CLIENT OFF|USER|ADMIN
Unless you are troubleshooting a particular problem, the trace level should be OFF. Other choices are USER, for a moderately detailed trace report, and ADMIN, for more extensive trace information.
Note: After troubleshooting your connection problem, turn trace level back to OFF. Leaving the trace facility set to USER or ADMIN can impact performance.
Status Monitor> SET TRACE_FILE_CLIENT file_name
You can change the name for the trace file with this command. In most operating systems, the trace file name is automatically appended with the suffix .TRC. You do not need to enter that suffix in the field.
Status Monitor> SET TRACE_DIRECTORY_CLIENT directory_path
You can change the directory to which the client trace file is written with this command. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
Status Monitor> SET TNSPING.TRACE_LEVEL OFF|USER|ADMIN
Unless you are troubleshooting a particular problem, the trace level should be OFF. Other choices are USER, for a moderately detailed trace report, and ADMIN, for more extensive trace information.
Note: After troubleshooting your connection problem, turn trace level back to OFF. Leaving the trace facility set to USER or ADMIN can impact performance.
Status Monitor> SET TNSPING.TRACE_DIRECTORY directory_path
You can change the directory to which the TNSPING trace file is written with this command. Be sure that you have write permission to the directory you select.
Status Monitor> SET AUTOMATIC_IPC ON|OFF
Use this command to change whether or not the client should use an IPC connection before trying other protocols. The default is for IPC to be set to ON
Status Monitor> SET SQLNET.CLIENT_REGISTRATION unique_identifier
This command sets a unique identifier for this client machine. This identifier will be passed to the listener with any connection request and will be included in the Audit Trail. The identifier can be any alphanumeric string up to 128 characters long.
Status Monitor> RESOLVE_SERVICE_NAME service_name
The Client Status Monitor displays the address.
The Client Status Monitor will also attempt a connection using the TNSPING utility if you enter the following command:
Status Monitor> ATTEMPT_CONNECT service_name
The TNSPING utility will return a message stating whether the connection attempt was successful, and how long it took.
|
Prev Next |
Copyright © 1996 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |