| Oracle® Database Java Developer's Guide 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B12021-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Java Developer's Guide 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B12021-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
You can increase your Java application performance through one of the following methods:
The Java language was designed for a platform-independent, secure development model. To accomplish these goals, some execution performance was sacrificed. Translating Java bytecodes into machine instructions degrades performance. To regain some of the performance loss, you may choose to natively compile certain classes. For example, you may decide to natively compile code with CPU intensive classes.
Without native compilation, the Java code you load to the server is interpreted, and the underlying core classes upon which your code relies (java.lang.*) are natively compiled.
Native compilation provides a speed increase ranging from two to ten times the speed of the bytecode interpretation. The exact speed increase is dependent on several factors, including:
Because Java bytecodes were designed to be compact, natively compiled code can be considerably larger than the original bytecode. However, because the native code is stored in a shared library, it is shared among all users of the database.
Most JVMs use Just-In-Time compilers that convert the Java bytecodes to native machine instructions when methods are invoked. The Accelerator uses an Ahead-Of-Time approach to recompiling the Java classes.
This static compilation approach provides a large, consistent performance gain, regardless of the number of users or the code paths they traverse on the server. After compilation, the tool loads the statically compiled libraries into Oracle Database, which are then shared between users, processes, and sessions.
Most Ahead-Of-Time native compilers compile directly into a platform-dependent language. For portability requirements, this was not feasible. Figure 10-1 illustrates how the Accelerator translates the Java classes into a version of C that is platform-independent. The C code is compiled and linked to supply the final platform-dependent, natively compiled shared libraries or DLLs.
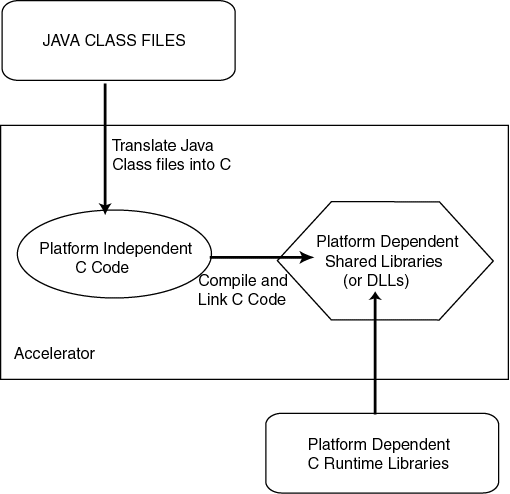
Text description of the illustration ncomp.gif
Given a JAR file, the Accelerator performs the following:
The Accelerator translates, compiles, and links the retrieved classes on the client. For this reason, you must natively compile on the intended platform environment to which this application will be deployed. The result is a single deployment JAR file for all classes within the project.
$ORACLE_HOME/javavm/admin directory.
All core Java class libraries and Oracle-provided Java code within Oracle Database is natively compiled for greater execution speed. Java classes exist as shared libraries in $ORACLE_HOME/javavm/admin, where each shared library corresponds to a Java package. For example, orajox10java_lang.so on Solaris and orajox10java_lang.dll on Windows NT hold java.lang classes. Specifics of packaging and naming can vary by platform. The OracleJVM uses natively compiled Java files internally and opens them, as necessary, at runtime.
The Accelerator can be used by Java application products that need performance increased and are deployed in Oracle Database. The Accelerator command-line tool, ncomp, natively compiles your code and loads it in Oracle Database. However, in order to use ncomp, you must first provide some initial setup.
You must install the following before invoking Accelerator:
ncomp.System*.properties file located in the $ORACLE_HOME/javavm/jahome directory. Since the compiler and linker information is platform-specific, the configuration for these items is detailed in the README for your platform.ncomp the following role and security permissions:
|
Note: DBA role contains both the |
JAVA_DEPLOY: The user must be assigned to the JAVA_DEPLOY role in order to be able to deploy the shared libraries on the server, which both the ncomp and deploync utilities perform. For example, the role is assigned to DAVE, as follows:
SQL> GRANT JAVA_DEPLOY TO DAVE;
FilePermission: Accelerator stores the shared libraries with the natively compiled code on the server. In order for Accelerator to store these libraries, the user must be granted FilePermission for read and write access to directories and files under $ORACLE_HOME on the server. One method for granting FilePermission for all desired directories is to grant the user the JAVASYSPRIV role, as follows:
SQL> GRANT JAVASYSPRIV TO DAVE;
See Chapter 9, "Security For Oracle Database Java Applications" for more information JAVASYSPRIV and granting FilePermission.
The following sections show how to do basic native compilation using Accelerator.
All the Java classes contained within a JAR file must already be loaded within the database. Execute the ncomp tool to instruct Accelerator to natively compile all these classes. The following code natively compiles all classes within the pubProject.JAR file:
ncomp -user scott/tiger pubProject.JAR
If you change any of the classes within this JAR file, Accelerator recompiles the shared library for the package that contains the changed classes. It will not recompile all shared libraries. However, if you want all classes within a JAR file to be recompiled--regardless of whether they were previously natively compiled--execute ncomp with the -force option, as follows:
ncomp -user scott/tiger -force pubProject.JAR
Accelerator, implemented within the ncomp tool, natively compiles all classes within the specified JAR, ZIP, or list of classes. Accelerator natively compiles these classes and places them into shared libraries according to their package. Note that these classes must first be loaded into the database.
If the classes are designated within a JAR file and have already been loaded in the database, you can natively compile your Java classes by executing the following:
ncomp -user SCOTT/TIGER myClasses.jar
There are options that allow you control over how the details of native compilation are handled.
ncomp [ options ] <class_designation_file> -user | -u <username>/<password>[@<database_url>] [-load] [-projectDir | -d <project_directory>] [-force] [-lightweightDeployment] [-noDeploy] [-outputJarFile | -o <jar_filename>] [-thin] [-oci | -oci8] [-update] [-verbose]
|
Note: These options are demonstrated within the scenarios described in "Native Compilation Usage Scenarios". |
Table 10-1 summarizes the ncomp arguments. The <class_designation_file> can be a <file>.jar, <file>.zip, or <file>.classes.
| Argument | Description and Values |
|---|---|
|
|
The full path name and file name of a JAR file that contains the classes that are to be natively compiled. If you are executing in the directory where the JAR file exists and you do not specify the - |
|
|
The full path name and file name of a ZIP file that contains the classes that are to be natively compiled. If you are executing in the directory where the ZIP file exists and you do not specify the - |
|
|
The full path name and file name of a classes file, which contains the list of classes to be natively compiled. If you are executing in the directory where the classes file exists and you do not specify the - |
|
|
Specifies a user, password, and database connect string; the files will be loaded into this database instance. The argument has the form |
|
|
The native compilation is performed on all classes. Previously compiled classes are not passed over. |
|
|
Provides an option for deploying shared libraries and native compilation information separately. This is useful if you need to preserve resources when deploying. See "lightweightDeployment" for more information. |
|
|
Executes |
|
|
All natively compiled classes output into a deployment JAR file. This option specifies the name of the deployment JAR file and its destination directory. If omitted, the |
|
|
Specifies that the native compilation results only in the output deployment JAR file, which is not deployed to the server. The resulting deployment JAR can be deployed to any server using the deploync tool. |
|
|
The database URL that is provided on the - |
|
|
The database URL that is provided on the -user option uses an OCI URL address for the database URL syntax. However, if neither - |
|
|
Specifies the full path for the project directory. If not specified, Accelerator uses the directory from which |
|
|
If you add more classes to a <class_designation_file> that has already been natively compiled, this flag informs Accelerator to update the deployment JAR file with the new classes. Thus, Accelerator compiles the new classes and adds them to the appropriate shared libraries. The deployment JAR file is updated. |
|
|
Output native compilation text with detail. |
The permissible forms of @<database> depend on whether you specify -oci or -thin; -oci is the default.
-oci: @<database> is optional; if you do not specify, then ncomp uses the user's default database. If specified, then <database> can be a TNS name or a Oracle Net Services name-value list.-thin: @<database> is required. The format is <host>:<lport>:<SID>.
Accelerator places compilation information and the compiled shared libraries in one JAR file, copies the shared libraries to $ORACLE_HOME/javavm/admin directory on the server, and deploys the compilation information to the server. If you want to place the shared libraries on the server yourself, you can do so through the lightweightDeployment option. The lightweightDeployment option enables you to do your deployment in two stages:
noDeploy and -lightweightDeployment options. This creates an deployment JAR file with only ncomp information, such as transitive closure information. The shared libraries are not saved within the deployment JAR file. Thus, the deployment JAR file is much smaller.Any errors that occur during native compilation are printed to the screen. Any errors that occur during deployment of your shared libraries to the server or during runtime can be viewed with the statusnc tool or by referring to the JACCELERATOR$DLL_ERRORS table.
If an error is caught while natively compiling the designated classes, Accelerator denotes these errors, abandons work on the current package, and continues its compilation task on the next package. The native compilation continues for the rest of the packages. The package with the class that contained the error will not be natively compiled at all.
After fixing the problem with the class, you can choose to do one of the following:
If you choose not to recompile the classes, but to load the correct Java class into the database instead, then the corrected class and all classes that are included in the resolution validation for that class--whether located within the same shared library or a different shared library--will be executed in interpreted mode. That is, the JVM will not run these classes natively. All the other natively compiled classes will continue to execute in native format. When you execute the statusnc command on the reloaded class or any of its referred classes, they will have a
NEED_NCOMPING status message.
Possible errors for a Java class:
Possible errors for deployment of native compilation JAR file:
The following scenarios demonstrate how you can use each of the options for the ncomp tool can be used:
If all classes are loaded into the database and you have completed your testing of the application, you can request Accelerator to natively compile the tested classes. Accelerator takes in a JAR, ZIP, or list of classes to determine the packages and classes to be included in the native compilation. The Accelerator then retrieves all of the designated classes from the server and natively compiles them into shared libraries--each library containing a single package of classes.
Assuming that the classes have already been loaded within the server, you execute the following command to natively compile all classes listed within a class designation file, such as the pubProject.jar file, as follows:
ncomp -user SCOTT/TIGER pubProject.jar
If you change any of the classes within the class designation file and ask for recompilation, Accelerator recompiles only the packages that contain the changed classes. It will not recompile all packages.
Once you have tested the designated classes, you may wish to natively compile them on a host other than the test machine. Once you transfer the designated class file to this platform, the classes in this file must be loaded into the database before native compilation can occur. The following loads the classes through loadjava and then executes native compilation for the class designation file--pubProject.jar:
ncomp -user SCOTT/TIGER@dbhost:5521:orcl -thin -load pubProject.jar
If you want all classes within a class designation file to be recompiled--regardless of whether they were previously natively compiled--execute ncomp with the -force option. You might want to use the -force option to ensure that all classes are compiled, resulting in a deployment JAR file that can be deployed to other Oracle Database instances. You can specify the native compilation deployment JAR file with the -outputJarFile option. The following forces a recompilation of all Java classes within the class designation file--pubProject.jar--and creates a deployment JAR file with the name of pubworks.jar:
ncomp -user SCOTT/TIGER -force -outputJarFile pubworks.jar pubProject.jar
The deployment JAR file contains the shared libraries for your classes, and installation classes specified to these shared libraries. It does not contain the original Java classes. To deploy the natively compiled deployment JAR file to any Oracle Database (of the appropriate platform type), you must do the following:
pubProject.jar file would be loaded into the database using the loadjava tool.By default, the Accelerator uses the directory where ncomp is executed as its build environment. The Accelerator downloads several class files into this directory and then uses this directory for the compilation and linking process.
If you do not want to have Accelerator put any of its files into the current directory, create a working directory, and specify this working directory as the project directory with the -projectDir option. The following directs Accelerator to use /tmp/jaccel/pubComped as the build directory. This directory must exist before specifying it within the -projectDir option. Accelerator will not create this directory for you.
ncomp -user SCOTT/TIGER -projectDir /tmp/jaccel/pubComped pubProject.jar
You can specify one or more classes that are to be natively compiled, within a text-based <file>.classes file. Use the following Java syntax to specify packages and/or individual classes within this file:
import com.myDomain.myPackage.*; import com.myDomain.myPackage.mySubPackage.*;
import com.myDomain.myPackage.myClass;
Once explicitly listed, specify the name and location of this class designation file on the command line. Given the following pubworks.classes file:
import com.myDomain.myPackage.*; import com.myDomain.hisPackage.hisSubPackage.*; import com.myDomain.herPackage.herClass; import com.myDomain.petPackage.petClass;
The following directs Accelerator to compile all classes designated within this file: all classes in myPackage, hisSubPackage and the individual classes, herClass and myClass. These classes must have already been loaded into the database:
ncomp -user SCOTT/TIGER /tmp/jaccel/pubComped/pubworks.classes
If you change any of the classes within this JAR file, Accelerator will only recompile shared libraries that contain the changed classes. It will not recompile all shared libraries designated in the JAR file. However, if you want all classes within a JAR file to be recompiled--regardless of whether they were previously natively compiled--you execute ncomp with the -force option, as follows:
ncomp -user scott/tiger -force pubProject.JAR
You can deploy any deployment JAR file with the deploync command. This includes the default output JAR file, <file>_depl.jar or the JAR created when you used the ncomp -outputJarFile option. The operating system and Oracle Database version must be the same as the platform where it was natively compiled.
|
Note: The list of shared libraries deployed into Oracle Database are listed within the |
deploync [options] <deployment>.jar -user | -u <username>/<password>[@<database_url>] [-projectDir | -d <project_directory>] [-thin] [-oci | -oci8]
Table 10-2 summarizes the deploync arguments.
Deploy the natively compiled deployment JAR file pub.jar to the dbhost database as follows:
deploync -user SCOTT/TIGER@dbhost:5521:orcl -thin /tmp/jaccel/PubComped/pub.jar
After the native compilation is completed, you can check the status for your Java classes through the statusnc command. This tool will print out--either to the screen or to a designated file--the status of each class. In addition, the statusnc tool always saves the output within the JACCELERATOR$STATUS table. The values can be the following:
statusnc [ options ] <class_designation_file> -user <user>/<password>[@database] [-output | -o <filename>] [-projectDir | -d <directory>] [-thin] [-oci | -oci8]
Table 10-3 summarizes the statusnc arguments. The <class_designation_file> can be a <file>.jar, <file>.zip, or <file>.classes.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The full path name and file name of a JAR file that was natively compiled. |
|
|
The full path name and file name of a ZIP file that was natively compiled. |
|
|
The full path name and file name of a classes file, which contains the list of classes that was natively compiled. See "Natively Compiling Specific Classes" for a description of a classes file. |
|
|
Specifies a user, password, and database connect string where the files are loaded. The argument has the form |
|
|
Designates that the |
|
|
Specifies the full path for the project directory. If not specified, Accelerator uses the directory from which |
|
|
The database URL that is provided on the - |
|
|
The database URL that is provided on the - |
statusnc -user SCOTT/TIGER -output pubStatus.txt /tmp/jaccel/PubComped/pub.jar
The typical and custom database installation process furnishes a database that has been configured for reasonable Java usage during development. However, runtime use of Java should be determined by the usage of system resources for a given deployed application. Resources you use during development can vary widely, depending on your activity. The following sections describe how you can configure memory, how to tell how much SGA memory you are using, and what errors denote a Java memory issue:
You can modify the following database initialization parameters to tune your memory usage to reflect more accurately your application needs:
SHARED_POOL_SIZE--Shared pool memory is used by the class loader within the JVM. The class loader uses an average of about 8 KB for each loaded class. Shared pool memory is used when loading and resolving classes into the database. It is also used when compiling source in the database or when using Java resource objects in the database.
The memory specified in SHARED_POOL_SIZE is consumed transiently when you use loadjava. The database initialization process (executing initjvm.sql against a clean database, as opposed to the installed seed database) requires SHARED_POOL_SIZE to be set to 50 MB as it loads the Java binaries for approximately 8,000 classes and resolves them. The SHARED_POOL_SIZE resource is also consumed when you create call specifications and as the system tracks dynamically loaded Java classes at runtime.
JAVA_POOL_SIZE--The OracleJVM memory manager allocates all other Java state during runtime execution from the amount of memory allocated using JAVA_POOL_SIZE. This memory includes the shared in-memory representation of Java method and class definitions, as well as the Java objects migrated to session space at end-of-call. In the first case, you will be sharing the memory cost with all Java users. In the second case, in a shared server, you must adjust JAVA_POOL_SIZE allocation based on the actual amount of state held in static variables for each session. See "Java Pool Memory" for more information on JAVA_POOL_SIZE.JAVA_SOFT_SESSIONSPACE_LIMIT--This parameter allows you to specify a soft limit on Java memory usage in a session, which will warn you if you must increase your Java memory limits. Every time memory is allocated, the total memory allocated is checked against this limit.
When a user's session-duration Java state exceeds this size, OracleJVM generates a warning that is written into the trace files. While this warning is simply an informational message and has no impact on your application, you should understand and manage the memory requirements of your deployed classes, especially as they relate to usage of session space.
JAVA_MAX_SESSIONSPACE_SIZE--If a user-invokable Java program executing in the server can be used in a way that is not self-limiting in its memory usage, this setting may be useful to place a hard limit on the amount of session space made available to it. The default is 4 GB. This limit is purposely set extremely high to be normally invisible.
When a user's session-duration Java state attempts to exceeds this size, your application can receive an out-of-memory failure.
Oracle Database's unique memory management facilities and sharing of read-only artifacts (such as bytecodes) enables HelloWorld to execute with a per-session incremental memory requirement of only 35 KB. More stateful server applications have a per-session incremental memory requirement of approximately 200 KB. Such applications must retain a significant amount of state in static variables across multiple calls. Refer to the discussion in the "End-of-Call Migration" section for more information on understanding and controlling migration of static variables at end-of-call.
You can set the defaults for JAVA_POOL_SIZE and SHARED_POOL_SIZE in the database installation template. The Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) allows you to modify these values within the Memory section, as shown below in Figure 10-2.
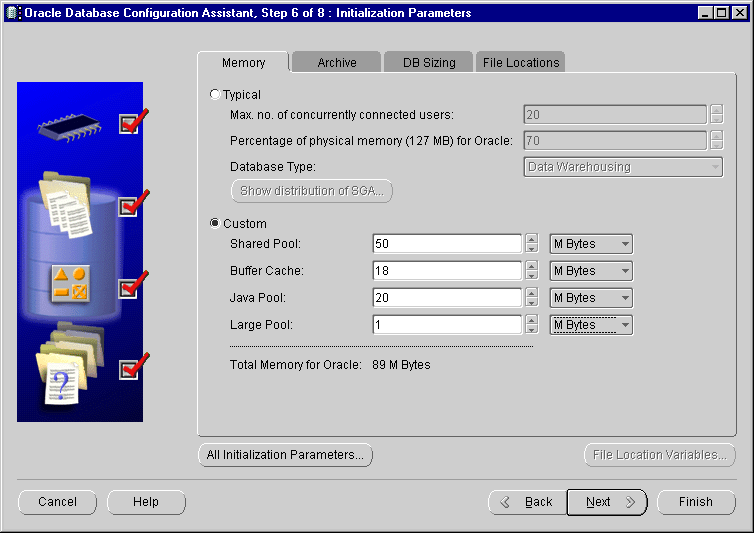
Text description of the illustration dbca_poo.gif
Java pool memory is used in server memory for all session-specific Java code and data within the JVM. Java pool memory is used in different ways, depending on what mode the Oracle Database server is running in.
The following is what constitutes the Java pool memory used within a dedicated server:
This includes read-only memory, such as code vectors, and methods. In total, this can average about 4 KB-8 KB for each class.
For a dedicated server, this is stored in UGA within the PGA--not within the SGA.
Under dedicated servers, the total required Java pool memory depends on the applications running and may range between 10 and 50 MB.
The following is what constitutes the Java pool memory used within a shared server:
This includes read-only memory, such as vectors, and methods. In total, this can average about 4 KB-8 KB for each class.
Because Java pool memory size is fixed, you must estimate the total requirement for your applications and multiply by the number of concurrent sessions the applications want to create to calculate the total amount of necessary Java pool memory. Each UGA grows and shrinks as necessary; however, all UGAs combined must be able to fit within the entire fixed Java pool space.
Under shared servers, this figure could be large. Java-intensive, multi-user benchmarks could require more than 100 MB.
|
Note: If you are compiling code on the server, rather than compiling on the client and loading to the server, you might need a bigger JAVA_POOL_SIZE than the default 20 MB. |
You can find out how much of Java pool memory is being used by viewing the V$SGASTAT table. Its rows include pool, name, and bytes. Specifically, the last two rows show the amount of Java pool memory used and how much is free. The total of these two items equals the number of bytes that you configured in the database initialization file.
SVRMGR> select * from v$sgastat; POOL NAME BYTES ----------- -------------------------- ---------- fixed_sga 69424 db_block_buffers 2048000 log_buffer 524288 shared pool free memory 22887532 shared pool miscellaneous 559420 shared pool character set object 64080 shared pool State objects 98504 shared pool message pool freequeue 231152 shared pool PL/SQL DIANA 2275264 shared pool db_files 72496 shared pool session heap 59492 shared pool joxlod: init P 7108 shared pool PLS non-lib hp 2096 shared pool joxlod: in ehe 4367524 shared pool VIRTUAL CIRCUITS 162576 shared pool joxlod: in phe 2726452 shared pool long op statistics array 44000 shared pool table definiti 160 shared pool KGK heap 4372 shared pool table columns 148336 shared pool db_block_hash_buckets 48792 shared pool dictionary cache 1948756 shared pool fixed allocation callback 320 shared pool SYSTEM PARAMETERS 63392 shared pool joxlod: init s 7020 shared pool KQLS heap 1570992 shared pool library cache 6201988 shared pool trigger inform 32876 shared pool sql area 7015432 shared pool sessions 211200 shared pool KGFF heap 1320 shared pool joxs heap init 4248 shared pool PL/SQL MPCODE 405388 shared pool event statistics per sess 339200 shared pool db_block_buffers 136000 java pool free memory 30261248 java pool memory in use 19742720 37 rows selected.
If you run out of memory while loading classes, it can fail silently, leaving invalid classes in the database. Later, if you try to invoke or resolve any invalid classes, you will see ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundException exceptions being thrown at runtime. You would get the same exceptions if you were to load corrupted class files. You should perform the following:
loadjava -force option to force the new class being loaded to replace the class already resident in the server.loadjava -resolve option to attempt resolution of a class during the load process. This allows you to catch missing classes at load time, not run time.select * from user_objects where object_name = dbms_java.shortname('');
The STATUS field should be "VALID". If loadjava complains about memory problems or failures such as "connection lost", increase SHARED_POOL_SIZE and JAVA_POOL_SIZE, and try again.